Purpose and Scope
The principles, rules and procedures set out in these Program Grant Guidelines (Grant Guidelines or PGG) govern the award and administration by the Millennium Challenge Account Entity (MCA Entity) or other entity, excluding the Millennium Challenge Corporation (MCC) and any other United States Government agency, of funding assistance that is granted to implement the Projects funded by MCC (Project or Projects) under Millennium Challenge Compacts (Compact or Compacts) and grant and implementation agreements entered into pursuant to Section 609(g) of the Millennium Challenge Act (Act), unless MCC in the Compact agrees to the use of alternative award and administration Grant procedures.Unless stipulated otherwise in the relevant Threshold Program Grant Agreement, these Grant Guidelines apply to MCC Threshold Programs funded pursuant to Section 616 of the Act.[[References to “Compact” in these Grant Guidelines apply in the same manner to “Threshold Programs”.]]
The PGG governs all Grants made by MCA Entities, including non-leveraged grants, leveraged grants, and program partnership grants. Additional guidance on developing and implementing the three categories of grants will be provided. The PGG is a policy guidance document for MCA Entities implementing Grant Programs, as this term is defined herein.
Authorities
Statutory Authority
Section 609(b)(1)(I) of the Millennium Challenge Act of 2003, as amended (Public Law [P.L.] No. 108-199, Division D, codified at 22 United States Code [U.S.C.] 7701, et seq.)Federal Government Regulations, Standards, and Other Guidance
Not applicableRelated MCC Policies and Procedures
- Cost Principles for Government Affiliates
- Policy on Preventing, Detecting, and Remediating Fraud and Corruption in MCC Operations
- Guidelines for Accountable Entities and Implementation Structure
- MCC Program Procurement Guidelines
- Standards for Corporate Marking and Branding
- Standards for Global Marking
- Technical Specifications for Infrastructure Project Signs
- MCC Partnership Navigator
- MCC Leverage GrantsFacility Operations Manual
- M&E Policy
- MCC Counter-Trafficking in Persons (C-TIP) Policy
- MCC Environmental Guidelines
- MCC Gender Policy
- Guidelines for Economic and Beneficiary Analysis
Effective Date
These Grant Guidelines become effective on the date approved and supersede all previous policies and procedures issued by MCC related to award and administration of Grants by MCA Entities.Acronyms
- Call for Concept Papers (CFCP)
- Millennium Challenge Account Entity (MCA Entity)
- Millennium Challenge Corporation (MCC)
- Notice of Funding Opportunity (NOFO)
- Program Grant Guidelines (PGG)
- Request for Applications (RFA)
Definitions
- “Applicant” means an entity that submits an Application asking for an MCC-funded Grant from an MCA Entity.
- “Application” means the written[[All references to “written” in these Grant Guidelines include electronic submissions including emails.]] document, including all subsequent additional information and modifications, submitted by an Applicant as required to assess the technical merit of the Application, the capability of the Applicant and the proposed budget. Applications may be unsolicited or submitted in response to a Request for Applications.
- “Application Appraisal Report” means the report submitted to the Selection Committee that includes all the information that the MCA Entity has developed regarding the Application. Particularly, this includes the Merit Review Advisory Report, the Capability Risk Assessment Report and the Grant Budget Assessment Report.
- “Call for Concept Papers” means an announcement publicly advertised by the MCA Entity requesting submission of Concept Papers. This is the first step in the Two-Step Concept Paper/RFA Grant Award Procedure.
- “Call for Information” means an announcement publicly advertised by the MCA Entity requesting information that it needs to develop a Grant Program or to create effective documents announcing a Grant Program. This tool is used during the planning stage of a Grant cycle.
- “Co-Creation” means the process of collaboration between the MCA Entity and potential Grantee(s) in designing Grant Programs or developing documents. This can occur at any stage of the Grant Award process depending upon the requirements of the Grant Award Procedure that is followed. When using Co-Creation, the MCA Entity cooperates with the entity on the development or modification of a submission (Concept Paper, Concept Note or Application).This contrasts with Discussions, which is a tool to provide feedback on an entity’s submission so that the entity can, acting on its own, improve subsequent submissions.
- “Compact End Date” means the last day of the Compact Term (as defined in the Compact).
- “Concept Note” means the written document submitted by a Proposer in response to a Notice of Funding Opportunity. This is the first submission in the Two-Step Concept Note/RFA Grant Award Procedure, a procedure that is used to seek innovative approaches for carrying out a Grant Program.
- “Concept Paper” means the written document submitted by a Proposer in response to a Call for Concept Papers. This is the first submission in the Two-Step Concept Paper/RFA Grant Award Procedure, a procedure that is used when Grant Activities are already well-defined.
- “Cooperation Agreement” means a type of Grant relationship in which the MCA Entity is significantly involved with the Grantee in carrying out the Grant Activities being funded. MCA Cooperation Agreements also include other features such as a Partnership Advisory Committee, where multiple stakeholders convene to set direction, track progress and problem solve to gain better results, and mandatory partner contributions.
- “Cost Reimbursement Grant” means the type of Grant relationship in which the MCA Entity disburses the Grant funds by reimbursing the Grantee for allowable costs incurred up to a ceiling amount.
- “Cost Share” means the resources a Recipient contributes to the total cost of the Grant Activities. Cost Share is not a mandatory or uniform requirement for MCA Grant Programs generally but could be a deemed mandatory requirement for a specific MCA Grant Program.
- “Direct Request” means the Grant Award Procedure in which the MCA Entity invites one entity to submit an Application for a particular Grant.
- “Discussions” means a process of dialogue between an MCA Entity and a Proposer or an Applicant aimed at improving the entity’s subsequent submissions. Discussions provide feedback on an entity’s submission so that the entity can, acting on its own, improve its subsequent submissions as compared with Co-Creation during which the MCA Entity cooperates with the entity on the development or modification of a submission (Concept Paper, Concept Note or Application).
- “Fixed Amount Grant” means a Grant relationship in which the MCA Entity commits to a specific level of support to carry out defined Grant Activities based upon an assessment of reasonable cost determined in advance of signing the Grant Agreement.
- “Fixed Amount Grant with Reimbursement for Direct Costs” means a Grant relationship in which the MCA Entity supports the Grantee through two categories of disbursement. The Grant Agreement commits to (1) a specific level of support for a portion of the Grant based upon an assessment of reasonable cost determined in advance of signing the Grant Agreement and (2) reimbursement of actual cost of certain identified direct costs.
- “Grant” means a transfer of MCC assistance in cash or in kind made for a specific purpose by an MCA Entity under any form of Grant Agreement defined in these Grant Guidelines.
- “Grant Activities” means the actions that a Grantee undertakes to carry out a Grant using its best efforts to fulfill the purpose of a Grant including in-kind, Cost Share or Leverage plus any actions promised by the MCA Entity under a Grant Agreement that includes in-kind assistance.
- “Grant Agreement” means the written legal document that establishes the relationship between the MCA Entity and the Grantee. It sets forth the commitment of the MCA Entity to transfer funding assistance to the Grantee for a specific purpose subject to satisfaction of conditions for disbursement and other applicable terms and conditions. Cooperative Agreements, Cooperation Agreements and Program Partnership Agreements are forms of Grant Agreements.
- “Grant Award” means the award of MCC funding assistance made by the MCA Entity to an entity under the terms of a Grant Agreement.
- “Grant Award Procedure(s)” means all the actions undertaken by the MCA Entity to request and receive Applications and select Applicants for Grant Award. These Grant Guidelines include several Grant Award Procedures from which the MCA Entity can choose depending upon the circumstances as explained in the conditions for use under each Grant Award Procedure.
- “Grant Budget Narrative” means the explanation of the estimated costs by line item or category set out in the Grant Budget. The Grant Budget Narrative should set forth a detailed breakdown of costs and explain how the costs associated with each line item or category relate to carrying out the Grant Activities.
- “Grant Facility” means a specific organizational and procedural structure for disbursing MCC Compact funds and awarding multiple Grants through an open and competitive process. Grant Facilities are governed by a Grant Facility Operations Manual and are usually administered from planning to closeout by a professional Grant Facility Manager procured by the MCA Entity or its predecessor entity. Proposed projects and potential Grantees are evaluated using a standardized set of screening and due diligence tools that assess financial sustainability, management and implementation capacity, technical feasibility, market impact, and contribution to economic growth and poverty reduction. If a Grant Facility Manager is required to administer the program, it should be acquired and mobilized by the date the Compact enters into force.
- “Grant Guidelines” means these MCC Program Grant Guidelines.
- “Grant Manager” or “Grant Facility Manager” means the personnel hired or a firm contracted by the MCA Entity to manage one or more Grant Programs.
- “Grants Operations Manual” or “Grant Facility Operations Manual” means the book of guidance for implementing non-leverage grant that includes interpretive and instructional materials plus forms and templates.
- “Grant Program” means a program of assistance that the MCA Entity is implementing to achieve certain objectives, results, indicators and targets set out in the Compact and its implementing documents. It may take the form of a Grant Facility, an individual Grant or multiple Grants that each serve a public purpose.
- “Grant with Limited MCA Involvement” means a type of Grant relationship in which the MCA Entity is materially involved with the Grantee in carrying out only certain programmatic aspects of the Grant Activities being funded.
- “Grant with Special Conditions” means a type of Grant relationship that includes a provision in the Grant Agreement requiring the particular Grantee to satisfy certain requirements as a condition of Grant funding.
- “Grant with Substantial MCA Involvement” (Cooperative Agreement) means a type of Grant relationship in which the MCA Entity is materially involved with the Grantee in carrying out substantial programmatic aspects of the Grant Activities being funded.
- “Grantee” or “Recipient” means the entity that receives a Grant from an MCA Entity.
- “In-Kind Grant” means a type of Grant relationship in which the MCA Entity procures and furnishes directly to the Grantee certain goods, works and/or services (rather than funds) needed to carry out the Grant.
- “Leverage” means resources that a Grantee brings to a Partnership or Grant. Leverage may be in a variety of forms that provides anything of value that can be measured such as financial contributions, third party contributions, donated services or property, or intellectual property. Unlike Cost Share, Leverage is not audited.
- “MCA Board” means the governing body of the MCA Entity.
- “MCA Director of Grants” means the member of the MCA Entity senior management that is responsible for managing the award and administration of Grants awarded by the MCA Entity. When MCC approves implementation of a Grant Program, MCC will generally require that the MCA Entity employ an MCA Director of Grants who will serve as a member of the MCA Entity senior management. MCC may also permit one person to serve as both the MCA Director of Procurement and the MCA Director of Grants.MCC may also require that the Procurement Agent serve asa Grant Manager or include resources to support award and management of Grants.With respect to a Grant Program authorized under a Threshold Program, “MCA Director of Grants” means the member of the local country team who is capable of assuming the duties and responsibilities of an MCA Director of Grants as set out in these Grant Guidelines. “MCA Director of Grants” also means the persons or agents delegated by the MCA Director of Grants to act on his or her behalf.
- “MCA Entity” means the entity designated by the government of the country receiving assistance from the MCC as responsible for the oversight and management of implementation of the Compact on behalf of the government. MCA Entity includes any predecessor entity designated to represent the government during Compact development and up until the formal MCA Entity is set up and any successor entity that might be set up to represent the government until final closeout of the Compact. MCA Entity also means any entity designated by the government to implement a Threshold Program.
- “MCC Partnership Navigator” means the book of guidance and tools for implementing program partnerships, including interpretive and instructional materials plus forms and templates.
- “Memorandum of Negotiation” means the document prepared under certain conditions as a record of the negotiation of a Grant Agreement between a potential Grantee and the MCA Entity.
- “Merit Review” means the formal process of reviewing and analyzing the technical merit of an Application and may also be used to review technical merit of a Concept Note or a Concept Paper.
- “Milestone Disbursement Schedule” means the schedule for disbursing Grant funding assistance to a Grantee based upon the designated milestones achieved in carrying out the Grant.
- “Notice of Funding Opportunity” means an announcement publicly advertised by the MCA Entity requesting submission of Concept Notes. This is the first step in the Two-Step Concept Note/RFA Grant Award Procedure.
- “One-Step RFA” means the Grant Award Procedure that begins with the Request for Applications and is not preceded by a Call for Concept Papers.
- “Program Partnership” means a collaborative relationship between two or more entities – governmental or nongovernmental – in which the partners work together to achieve a common purpose or undertake a specific task and to share risks, responsibilities, resources, competencies, and benefits. The partners mutually determine the goals, structure, governance, roles, and responsibilities of their collaboration.
- “Partnership Advisory Committee” means a committee that includes members—beyond MCA and the Grantee—who are authorized to provide guidance to mobilize expertise or other resources for the Grant activity and to provide advice on the adaptation of the joint effort for successful outcomes under a Cooperation Agreement.
- “Pre-Announcement Survey” means a survey conducted by the MCA Entity to gain information and data it needs for developing a Grant Program and the documents offering funding assistance. This tool is used during the planning stage of a Grant cycle.
- “Program Income” means the gross income earned by a Grantee that is directly generated by the Grant supported activity or earned from the Grant during the period of the Grant Agreement.
- “Program Partnership Solicitation” means an MCA led Program Partnership Solicitation pathway that provides an open, fair, competitive and transparent process for awarding Partnerships funded by MCA Entities.
- “Proposed Grant Award” means the decision taken by the MCA Entity to make a Grant to an Applicant subject to negotiation of a Grant Agreement.
- “Proposer” means an entity that originates, develops and submits a Concept Note or a Concept Paper.
- “Recipient” means an entity that receives an assistance award.
- “Request for Applications” means the document that sets out all of the requirements for submitting an Application. When used for Simplified Grants and in the One-Step RFA Grant Award Procedure, this document will be publicly advertised. When used as the second step in two-stepGrant Award Procedures, this document will be sent to selected Proposers.
- “Selection Committee” means the group of individuals who identify Applicants for Proposed Grant Award taking into consideration the Application Appraisal Reports and the Grant Program Policy Factors and in compliance with the principles and requirements set out in these Grant Guidelines. In making this determination, the Selection Committee will prescribe the terms and conditions for negotiating Grant Agreements. This group also determines, taking into consideration Concept Paper Appraisal Reports or Concept Note Appraisal Reports, which Proposers will be invited to submit Applications.
- “Selection Committee Concept Selection Report” means the report issued by the Selection Committee setting out its determinations with justification identifying Proposers to be invited to submit Applications. Selection Committee Concept Selection Reports must be approved by MCC.
- “Selection Committee Grant Award Report” means the report issued by the Selection Committee setting out its determinations with justification identifying Proposed Grant Awards. Selection Committee Grant Award Reports must be approved by MCC.
- “Selection Committee Preliminary Report” means the report issued by the Selection Committee after review of Application Appraisal Reports instructing the MCA Director of Grants to enter into Discussions or Co-creation with a goal to improve the Applications before the Selection Committee determines to make Proposed Grant Award(s).
- “Simplified Grant” means Grant below a threshold value that is awarded using Grant procedures and documents appropriate for relatively low value Grants. This is both an award procedure and a type of Grant relationship.
- “Standard Grant” means a type of Grant relationship in which the MCA Entity conducts administrative oversight to assure that the terms and conditions of the Grant Agreement are met.
- “Subaward” means an award of funding assistance by a Recipient, serving as a pass-through entity, to another entity, the Sub-recipient.
- “Sub-grantee or Sub-recipient” means the entity that receives a Subaward. This does not include an individual that is a beneficiary of a Grant.
- “Threshold Programs” means the programs funded pursuant to Section 616 of the Act and intended to assist promising candidate countries to become Compact eligible by offering them the opportunity to demonstrate their commitment to just and democratic governance, economic freedom, and investments in their people.References to “Compact” in these Grant Guidelines apply in the same manner to “Threshold Programs”.
- “Two-Step Concept Note/RFA” means a Grant Award Procedure that begins with a Notice of Funding Opportunity requesting Concept Notes followed by a Request for Application inviting Applications from selected Proposers based upon review of Concept Notes.
- “Two-Step Concept Paper/RFA” means a Grant Award Procedure that begins with a Call for Concept Papers followed by a Request for Application inviting Applications from selected Proposers based upon review of Concept Papers.
- “Unsolicited Application” means an Application received by an MCA Entity that is not in response to a notice by the MCA Entity.
PART 1: Selection and Use of Program Grants
Grants: Must have intent-to-benefit Grantee and support public purpose[[See Guidance Note “Grants and Procurement Compared” for further information.]]A Grant is a transfer of financial assistance in cash or in-kind from an MCA Entity, the Grantor, to an eligible Grantee for a public purpose in furtherance of the Compact. The mission, programs and activities of the Grantee, the direct beneficiary of the financial assistance, must align with and be supportive of the MCA Entity’s mission, programs, or activities in a designated program area or sector pursuant to implementing the Compact.
Given this necessary alignment of interest, a Grant awarded by the MCA Entity serves a dual purpose. First, the financial assistance supports and benefits the Grantee directly as an intended beneficiary of the award. Simultaneously, the Grant empowers the Grantee to carry out a Grant Program in support of a public purpose. As an intended beneficiary of an award of financial assistance by reason of its mission, programs, and activities, a Grantee serves a public purpose supportive of a Compact and becomes a co-stakeholder in the outcome of the program or activity described in the Grant Agreement. The MCA Entity, as the Grantor, supports and fulfills a public purpose by assisting the Grantee.
Since the intent-to-benefit the Grantee in support of a public purpose is the critical feature of a Grant Program, the rational for supporting the Grantee or category of Grantees must be explained in the justification for using a Grant Program.
Grants: Must determine eligible category Grantees for each Grant Program
Since the intent-to-benefit a Grantee must be established, it follows that it is essential to identify the category of entities targeted for a potential award of financial assistance under a Grant Program. The mission, programs and activities of eligible entities must align with those of the MCA Entity with respect to the programmatic subject matter of the anticipated Grant Agreement. The scope of eligible entities for a Grant Program must be identified during the planning phase of the Grant cycle, explained in the justification for using a Grant Program, and made clear when the Grant Program is advertised.
The public purpose and the intent-to-benefit attributes of Grants do not necessarily preclude for-profit business entities from being an eligible Grantee in specific situations. However, a profit cannot be made on a Grant; Grant funds can be used only to cover the Grantee’s cost. A for-profit entity may act for other than for-profit purposes to support a public purpose or it may be eligible for an award of financial assistance where it is necessary to stimulate a commercial enterprise to undertake activities supportive of a public purpose. In situations like these, the MCA Entity may have the requisite intent-to-benefit a for-profit enterprise as an intended beneficiary of a transfer of financial assistance to advance a public purpose.
Grants: Award financial assistance through Grant Agreements
A Grant Agreement, the legal instrument used to award financial assistance to an eligible Grantee, creates the legal and operational relationship between the MCA Entity and the Grantee. It sets forth the conditions that govern the relationship of the parties as well as the conditions attached to the transfer, disbursement, and use of the financial assistance awarded to the Grantee. Under a Grant Agreement, the Grantee becomes a stakeholder in implementing the Compact with substantial programmatic responsibilities and autonomy.
The Grantee undertakes to use its “best efforts” to carry out the program or activity described in the Grant Agreement supportive of Compact objectives. Typically, the Grant Agreement gives the Grantee significant autonomy in carrying out the Grant Activities, while the MCA Entity exercises careful and thoughtful oversight. However, as circumstances require, the MCA Entity may set the terms of a Grant Agreement to participate in a more collaborative programmatic relationship and/or cost sharing (or co-financing) of a project that supports Compact objectives.
Grants: Support a wide range of Grant relationships and Grant Programs
These Grant Guidelines authorize several types of Grant Agreements providing the MCA Entity considerable flexibility to define its relationship with the Grantee in terms that best address the circumstances of the Grant Program and the capabilities of the Grantee.For example, the range of Grant Programs may run from an MCA Entity awarding a single Grant to carry out a single program activity to a large, multi-million-dollar Grant Facility that awards multiple Grants in order to achieve a programmatic objective.MCA Entity staffing to manage a Grant Program must be commensurate to the size and complexity of the Grant Program. A Grant Facility, for example, may require a contracted Grant Facility Manager, while a small Grant Program may only necessitate one dedicated MCA Entity staff to manage the Grants.
Grants: Must be justified by the MCA Entity and approved by MCC
The MCA Entity must justify its reasoning for entering into a Grant Agreement instead of a procurement. Grants are a form of assistance to a designated class of Recipients. MCA Entities should not use Grants to evade the legal requirements of the PPG or to offer support to suppliers and contractors selling goods, works or services to the MCA Entity. Moreover, a Grant Agreement should not be used to purchase goods, works or services for the MCA Entity because it neither requires performance nor provides the enforceable rights and remedies set out in the procurement contract for non-performance. In many Compacts the decision to use Grant Agreements to implement Projects is made and justified during Compact development; however, Grants may be used at any stage of the Compact, including during Compact development. A Grant Program is incorporated into the terms of the Compact[[References to Compact in this paragraph include any Compact development agreement signed between MCC and the partner government.]] and approved when the Compact is signed by MCC. However, in other cases, the determination to use a Grant Program to implement an activity under the Compact occurs after the Compact is signed. In such cases, the MCA Entity must seek MCC approval to use a Grant by documenting both that the use of a Grant Program is justified and that a Grant Agreement is the most appropriate arrangement to use to implement certain objectives of the Compact. Whether approved by MCC during Compact development and with the signing of the Compact or subsequently, use of a Grant Agreement, rather than a procurement contract, must be justified in a written document maintained in the Grant file and subject to review and audit.
PART 2: General Requirements
Guidelines
General Considerations
The MCA Entity is responsible for implementing Compact Projects. While implementation is primarily through procurement contracts, Grants may be a useful implementation mechanism to achieve certain Compact program objectives.[[See Guidance Note “Grants and Procurement Compared” for further information]] These Grant Guidelines provide specific rules and procedures to be followed in the award and administration of MCC-funded Grants and must be interpreted and applied consistent with the principle that open, competitive and fair procedures are used in a transparent manner in the award and administration of Grants, for the accomplishment of objectives under the Compact.The MCA Entity must ensure 1) that all Grants are carried out in furtherance of the Compact; 2) that all Grant Program and Grant Awards[[Grant Awards are approved by MCC within the context of MCC’s approval of the Selection Committee Grant Award Report and amendments thereto.]] that are funded with MCC funding, in whole or in part, directly or indirectly, are approved by MCC; and 3) that Grant Programs and Grant Awards comply with these Program Grant Guidelines and the MCC Cost Principles for Government Affiliates.
General Requirements, Conditions and Prohibitions
Anti-Fraud and Corruption Policy
The MCA Entity and all Recipients of MCC funding, including Grantees, must comply with MCC’s Policy on Preventing, Detecting and Remediating Fraud and Corruption in MCC Operations, also known as MCC’s Anti-Fraud and Corruption (AFC) Policy. The full text of the policy can be found here: AFC Policy. In brief, it prohibits asking for or accepting money or anything of value to award a Grant or to make any other decision involving an action by the MCA Entity, to avoid taking actions that benefit one’s self, relatives, friends, or former or future employers, and to report any suspicions that anyone else may be engaging in these or any other activities prohibited by the policy. Reports can be made to MCC or the Office of the Inspector General, through hotline@mcc.gov or through the means set out in the MCA Entity’s Grants Operations Manual.The MCA Entity including its employees, Board members, consultants, agents for fiscal, procurement and Grants, Grant Managers, Grant Facility Managers, executing entities, bidders, suppliers, contractors, subcontractors, potential Grantees, Grantees and Sub-grantees must comply with the AFC Policy and with applicable U.S. Government laws and regulations and MCC policies regarding purchasing, financial management, contract management and Grant management during the development, implementation and closure of the Compact.
The government of the MCA Entity will be required to reimburse MCC for any Grant funding that is lost due to fraud, corruption, or gross mismanagement by the Grantee including its employees, its Sub-grantees or its contractors or consultants irrespective of whether the MCA Entity is reimbursed funds by the Grantee.
Conflicts of Interest and Impartiality
Entities and individuals must avoid conflicts between their MCA Entity activities and their own financial interests. They must also avoid circumstances where a reasonable person would believe they cannot discharge their professional responsibilities impartially due to personal friendships, prior associations or affiliations, or other factors that would unfairly affect their judgment.Conflicts of Interest: Entities and individuals must not receive a Grant for an activity that would be in conflict with their prior or current obligations to other clients or donors, or that may place them in a position of being unable to carry out the terms and conditions of the Grant in the best interest of the MCA Entity. Any individual is deemed to have financial conflicts of interest when they are in a position that requires them to make objective decisions on behalf of the MCC funded program and they have business interests, relationships or obligations that might interfere with their judgment. Without limiting the generality of the foregoing, conflicts of interest are deemed to exist in the circumstances set forth below:
-
No MCA Entity staff or MCA Board member may use their position to obtain personal benefits or special consideration for themselves, their families, business associates, past (for at least the past three years) or future employers, or anyone else in the selection of Recipients, Sub-recipients or their contractors or suppliers.
-
No MCA Entity staff or MCA Board member may participate in the award or administration of a Grant supported by MCC funding if their participation would create financial conflicts of interest. Financial conflicts of interest arises if the individual employee or any member of their immediate family (includes spouse, domestic partner, sibling, parent, child, aunts, uncles and cousins to the first degree) would benefit from the selection of an entity for a Grant Award or the administration of the award to a Recipient.
Impartiality: MCA Entity staff and MCA Board members are required to discharge their professional obligations impartially. That means they are not to let considerations of friendship, prior affiliations with an organization or relationships affect their deliberations or decisions in any way. They must notify the General Counsel of the MCA Entity if there are circumstances where they think they cannot be impartial when considering a Grant application or dealing with a Recipient or where a third-person would perceive they cannot act impartially. Therefore:
- Any individual who serves as a member of a Merit Review Panel or of a Selection Committee must read, understand, disclose information relevant to conflicts of interest and impartiality and must sign the Certificate of Confidentiality and Impartiality.
A Proposer or Applicant for a Grant must notify the MCA Entity of any actual or potential conflicts of interest or perception that an MCA Entity staff member could not be impartial of which they are aware when participating in a Grant Award Procedure. The MCA Entity must include notice of this requirement in every notice of a Grant opportunity, namely Notice of Funding Opportunity, Call for Concept Papers and Request for Applications.
Every Recipient must have written policies and procedures in place to prevent financial conflicts of interest and require notification of perceptions of partiality. The Recipient’s written policies must include a provision that the staff, officers or agents of the Recipient or any member of their immediate families cannot receive a Subaward without disclosing the conflicts of interest and impartiality perception and following the Recipient’s written policy and procedures for mitigating the situation. The Recipient’s policies must also state that its staff, officers and agents must neither solicit nor accept gratuities, favors or anything of monetary value from Sub-recipients or prospective Sub-recipients.
Ineligible Activities
In issuing a notice of Grant opportunity, the MCA Entity may define the range and scope of activities for Grantees to carry out under the specific Grant Program. Notwithstanding the limitations set forth in the notice, the following activities are not eligible for support with MCC Grant funding assistance:- Activities that do not align with the Compact objectives;
- Activities classified as a Categorical Prohibition as defined in MCC’s Environmental Guidelines;
- Projects and/or activities that involve involuntary physical resettlement or involuntary economic displacement (as defined by IFC Performance Standard 5) of any project affected persons;
- Projects and/or activities that involve trafficking in persons or people subject to trafficking in persons (as defined by MCC’s Counter-Trafficking in Persons Policy);
- Projects and/or activities that involve the employment of children aged below 15 or children performing any work that is economically exploitative or that is likely to be hazardous to, or to interfere with the child’s education, or to be harmful to the child’s health or physical, mental, spiritual, moral or social development;
- Activities supporting and costs associated with any of the following items:
- Military equipment;
- Surveillance equipment;
- Commodities and services specifically for support of police or other law enforcement activities;
- Abortion equipment and services;
- Luxury goods and gambling equipment;
- Activities involving, promoting, or condoning violence by any individual, group, or government;
- Activities related to campaigns for public office;
- Lobbying directed at influencing public policy decisions of local, state, or national governments;
- Activities related to education, training, or informing audiences of any partisan policy or practice or candidate for office; and,
- Activities declared illegal under all applicable local laws, as well as any prohibited activities under the MCC Compact, including in support of costs unallowable under the MCC Cost Principles for Government Affiliates.
Ineligible Entities
In issuing a notice of Grant opportunity, the MCA Entity must define any limitations or restrictions on the type of entities that it is seeking to fund under the Grant Program. Notwithstanding the limitations set forth in the notice, the following entities are not eligible to receive an MCC-funded Grant from the MCA Entity or a Subaward.- Individuals;
- Political parties, groups or institutions, or their subsidiaries and affiliates;
- Organizations that advocate, promote or espouse anti-democratic policies or illegal activities under local law;
- National, state, and local government entities (Under certain circumstances public, publicly owned and publicly subsidized organizations might be eligible for Grant Award with MCC prior approval and for Subawards with prior approval of MCA Entity and MCC.);
- Faith-based organizations whose objectives are for religious purposes, and whose main objective for the use of Grant funding assistance is of a religious nature;
- Any person or entity that has been declared ineligible for participation in procurements funded with World Bank assistance, or that has been debarred or suspended from participations in procurements funded by the United States Federal Government, or that is otherwise prohibited by applicable United States law or Executive Order or United States policies including under any then‐existing antiterrorist policies are not eligible to apply for funding. The MCA Entity must follow the eligibility verification procedures in Part 10 of the Program Procurement Guidelines to determine eligibility and must document compliance with eligibility verification procedures prior to award and periodically after the award as required by Part 10 of the Program Procurement Guidelines;
- Entities deemed to have conflicts of interest including entities serving as the MCA Entity’s agents for fiscal, procurement and Grants, and the MCA Entity’s Grant Manager(s) and Grant Facility Manager(s); and,
- Public International Organizations[[USAID’s list of PIOs can be found here: https://www.usaid.gov/sites/default/files/documents/1876/308maa.pdf]] may receive Grant funding with the prior approval of MCC.
Program Income
Program income includes but is not limited to income from fees for services performed, the use or rental of real or personal property acquired under a Grant Award, the sale of commodities or items fabricated under a Grant Award, license fees and royalties on patents and copyrights, and principal and interest on loans made with Grant funds. Interest earned on advances of Grant funds is not program income. Program income does not include rebates, credits, discounts, and interest earned on any of them.Program Income must be either: (a) deducted from the total allowable cost of the Grant in determining the net allowable cost of the Grant, or (b) added to the funds that are committed to Grant Activities and applied to further the Grant objectives for the purposes, during the duration of the Grant and under the conditions of the Grant Award. The method of utilizing Program Income is at the discretion of the MCA Entity with approval of MCC and must be detailed in the Grant Agreement.
The Grantee must identify and track Program Income and notify the MCA Entity of source and amounts in its regular reports. To the extent possible, the opportunities for and anticipated amount of Program Income should be identified in the Grant Budget prior to award. For Fixed Amount Grants, the determination of the opportunities for and anticipated amount of Program Income should be identified and deducted from the MCA-funded portion of the Grant Award. Once the Grant Budget is fixed, however, and consistent with characteristics and reporting requirements of a Fixed Amount Grant, notification and reporting on actual Program Income derived and utilized is not required unless otherwise specified under the terms and conditions of the Grant or requested under an audit required by MCA or MCC.
References to MCC
The MCA Entity must use the following language (or similar language acceptable to MCC) when referring to MCC in Grant documents[[This provision will need to be modified appropriately for Threshold Program Grant documents.]]:The United States of America acting through the Millennium Challenge Corporation (MCC) and [insert country] acting through the government thereof (the Government) have entered into a Millennium Challenge Compact for Millennium Challenge Account assistance to help facilitate poverty reduction through economic growth in [insert country] (The Compact) in the amount of approximately [insert amount of Compact] USD (MCC Funding). The Government, acting through [insert full legal name of the MCA Entity] ([insert short version of MCA Entity]) intends to apply a portion of the MCC Funding to eligible disbursements under a Grant for which this [insert type of Grant document] is issued. Any disbursements made under the proposed Grant will be subject, in all respects, to the terms and conditions of the Compact and related documents, including restrictions on the use and distribution of MCC Funding. No party other than the Government and [insert short versions of the MCA Entity] will derive any rights from the Compact or have any claim to the proceeds of MCC Funding.
Language
English is the official language of MCC-funded Grant documents, unless MCC has agreed in writing to allow the use of French or Spanish. No other language may be used. All Grant Agreements, reports, and records must be in English unless a written waiver has been issued by MCC. When documents or notices are created in more than one language, the English version will control. All published notices and requests must be published in English and in the local language if different from English, where publication in the local language is important to increase transparency and participation. Even if a document is posted or advertised in the local language, all communication between MCA Entity and MCC must be conducted in English unless MCC has issued a waiver for the use of French or Spanish.Branding and Marking
The MCA Entity must manage the branding and marking requirements of MCC-funded assistance and consistently communicate two key messages to public audiences in their countries: MCC assistance supports poverty reduction with countries committed to improving the lives of their citizens; and the Compact Grant funding is made possible through the generosity of the people of the United States of America. MCC specific branding and marking requirements are set out in MCC’s MCA Branding Guidelines.The MCA Entity must ensure that all Grant Agreements reference the MCC branding and marking guidelines and require every Grantee to develop a branding and marking plan specific to its Grant and subject to MCA Entity approval. In exercising its oversight responsibilities, the MCA Entity must ensure that the Grantee implements its branding and marking plan as approved.
Retroactive Funding
MCC funds must not be applied to cover costs incurred by the Grantee before the Grant Agreement is signed by all parties.Waivers
On a case-by-case basis, MCC can waive specific provisions of these Grant Guidelines for a specific Grant or Grant Program. Each waiver must be in writing and must be effective only to the extent specifically set forth in such writing. Unless issued as an Interim Amendment, a waiver does not permanently change these Grant Guidelines but, rather, functions as a one-time exception necessary to support one or more Grants and applies only to the specific MCA Entity requesting the waiver. All waiver requests will be generated by the MCA Entity. All waivers must be issued formally by MCC approval prior to implementation.PART 3: Grant Award Processes
Grant Award Processes
MCA Entities must apply the following policies and procedures when selecting entities to receive MCC funding under a Grant Agreement.General Documents and Procedures
The Grant Award Procedures described in this section are general processes that will apply in awarding Grants as specified in the procedures described in Part 4 of these Grant Guidelines.- Grant Planning Before implementing a Grant Program, MCA Entities should conduct thorough research and analysis of the circumstances and surrounding conditions for assistance opportunities. To assist in this research, the MCA Entity may use various research tools including Pre-Announcement Surveys, outreach events and Calls for Information.
- Grants Operations Manual The MCA Entity will establish a Grants Operations Manual[[For Leverage Grant Facilities, MCA Entities should refer to the Leverage Grant Operations Manual and associated solicitation, selection and award processes for additional guidance. For Program Partnerships, please refer to the MCC Partnerships Navigator.]] for any Grant Program that awards more than one Grant. MCC provides MCA Entities with a template for the manual that must be adopted by the MCA Entity. The MCA Entity will adopt, subject to MCC approval, the Grants Operations Manual template and/or the Grant Facility Operations Manual template as tailored to the MCA Entity’s circumstances and Grant Programs. The Grants Operations Manual provides guidance, templates and procedures for the selection, award and administration of Grants implemented by the MCA Entity. If there is a conflict between the Grants Operations Manual and the PGG, the PGG takes precedence.
- Grants Schedule The MCA Entity will prepare quarterly a Grant Schedule of the Grant Programs it plans to launch pursuant to implementing the Compact (Grants Schedule). The Grant Schedule will cover a 12-month period. The Grants Schedule is analogous to the MCA Procurement Plan, a document required under the MCC Program Procurement Guidelines, and should be prepared alongside the Procurement Plan. The Grants Schedule must (i) list the Grant Programs that the MCA Entity has defined and plans to announce, (ii) identify the methods of Grant Award Procedures to be used to select Grantees for each Grant Program, and (iii) provide the proposed amount of total funds that the MCA Entity plans to make available for each Grant Program. Like the Procurement Plan, the Grants Schedule is a key program planning and implementation document prepared by the MCA Entity. It serves as a management tool for the MCA Entity to oversee the launch of Grant Programs and for MCC to monitor the MCA Entity’s approach to implementing Grant Programs funded under the Compact. The MCA Entity must not advertise any funding assistance until the Grant Program is set out in the Grants Schedule, adopted by the MCA Board and approved by MCC.
- Notice and Advertising
The MCA Entity has a duty to promote transparency and fairness and to encourage participation in the process of the selection of Grantees and the award of MCC-funded Grants. Consistent with this obligation, it must provide notice of Grant funding opportunities to the maximum extent practicable. Several types of notice documents are defined in these Grant Guidelines that the MCA Entity will use, as appropriate, when applying the various Grant Award Procedures.Except for publication of the Grants Schedule, and for Request for Applications, when issued as the second step in a two-step Grant Award Procedure, Grant Program notices must be posted in English at (1) the MCA Entity’s website (or such other appropriate website designated by the MCA Entity and approved by MCC) and (2) the Development Gateway Market website at dgMarket.In addition, the MCA Entity may submit a copy of notices to the commercial officer of the local US Embassy and any other appropriate Embassy. MCC may post such notices on SAM.gov and/or any other U.S. Government publication such as Grants.gov.In countries where the official language is other than English, notices must be posted in English, and also may be posted in the official local language of the country of the MCA Entity, on the MCA Entity’s website or any other website in the country with written approval from MCC. Even if a document is posted or advertised in the local language, all communication between MCA Entity and MCC must be conducted in English unless MCC has issued a waiver for the use of French or Spanish. No other language can be used for communications with MCC.The MCA Entity should also seek to post or publish notices in other forums relevant to the subject matter of the specific Grant Program, such as association journals and newsletters and social media forums. MCC, at its sole discretion, may give written instruction to the MCA Director of Grants that sets out additional advertising requirements for any specific Grant Program.
Types of Grant Notices
- General Notice of Grants Schedule The General Notice of the Grants Schedule is published quarterly and is updated as needed. The General Notice of Grants Schedule is intended to provide potential Applicants advance notice of funding opportunities so that they might begin to prepare for the opportunity. It also informs the public of the planned Grant Program that is intended to have a positive impact for the general welfare in their communities.
- Request for Applications (RFA)
The RFA provides the MCA Entity with a notice document to use when the MCA Entity is ready to request all the information it needs to conduct the selection procedure and make Grant Award decisions. Accordingly, the RFA is used in three different Grant Award Procedures:
- The RFA is the notice document in a simple and brief format to request short and simple Applications for Simplified Grants. Generally, this RFA will set out a specific deadline closing date after which no further submissions will be considered; however, it can be set up with an open-ended response time.
- The RFA is the notice document in the One-step RFA Grant Award Procedure. This RFA is used when the Grant Activities and the methods of carrying out the Grant are well-defined, and the information needed to conduct Capability Risk Assessment to rate the potential Grantee’s ability to carry out the Grant Activities can be clearly defined. Since this is used for Grant Programs above the Simplified Grant threshold, this RFA is more detailed and the prescribed Application format seeks more information than for Simplified Grants. This RFA may provide an open-ended response time or it may set out a specific deadline closing date after which no further submission will be considered.
- The RFA is the document used to seek Applications in the Two-step Concept Paper/RFA and Two-step Concept Note/RFA Grant Award Procedures as defined below. The RFA begins the second step in these two-step procedures. Under both procedures, the RFA is issued only to the Proposers that passed the initial review and screening based upon their Concept Note or Concept Paper, as relevant, that each Proposer submitted in the first step of the Grant Award Procedure. With the RFA the MCA Entity seeks Applications from Proposers, who from this point forward are referred to as Applicants.
- Call for Concept Papers (CFCP) The CFCP is the document used as the first step in Two-step Concept Paper/RFA Grant Award Procedure. This procedure is used when the MCA Entity seeks to provide funding assistance to one or more Grantees to use for well-defined Grant Activities. The CFCP asks for Concept Papers in a prescribed format from entities labeled Proposers. In contrast to the Concept Note which invites creativity in substance and process, the Concept Paper invites Proposers to focus on their approach to carry out the defined Grant Activities. A CFCP may provide an open-ended response time or it may set out a specific deadline closing date after which no further submission will be considered.
- Notice of Funding Opportunity (NOFO) The NOFO is a document used as the first step in Two-step Concept Note/RFA Grant Award Procedure. This procedure uses Concept Notes as opposed to Concept Papers. The MCA Entity uses a NOFO for a Grant Program intended to support a variety of creative approaches to achieve the objectives and outcomes of the Grant Program. Because the purpose of this document is to seek creative and varied responses, the content of the NOFO focuses on describing anticipated results rather than a description of Grant Activities. The NOFO may provide an open-ended response time or it may set out a specific deadline closing date after which no further submission will be considered.
- Clarifications and Amendments The MCA Entity should permit the entities applying for Grants to submit questions about the CFCP, NOFO and RFA issued by the MCA Entity. When it is necessary to clarify or amend an element of the document in question either in response to a question or for another reason, the MCA Entity must issue a timely notice of clarification or amendment so that all entities participating or interested in participating will benefit from the information and have sufficient time before the submission deadline to consider the change.
- Discussions The MCA Entity under the direction and supervision of the MCA Director of Grants may enter into Discussions with any Proposer or Applicant as permitted under the Grant Award Procedure being followed. The focus of the Discussions must be on improving subsequent submissions. Discussions can provide feedback on the technical merit of a Concept Note, Concept Paper or Application by pointing out technical weaknesses that should be improved, providing suggestions for improving capability and/or commenting on the proposed Grant Budget where costs are not allowable or seem unreasonable or unnecessary. Since Discussions are focused on improving what is in a Concept Note, Concept Paper or Application, Discussions are conducted with each selected Proposer or Applicant individually. Following Discussions, the Proposer or Applicant is given a deadline to provide additional information to include in its Concept Note, Concept Paper or Application. The Discussions process must be structured in a spirit of fairness. Accordingly, Discussions must be confidential and must be conducted in a manner that does not favor one Proposer or Applicant over another or is not detrimental to any Proposer or Applicant. Conducting Discussions with one Proposer or Applicant does not require engaging in Discussions with all.[[Fairness does not mean equal. Fairness means treating all Proposers and Applicants the same as necessary. For example, if the MCA Entity has funds to make three Grant Awards and one Application is very strong as submitted but two have weaknesses that need to be improved, then public interest is best served if the MCA Entity conducts Discussions with the two weaker Applicants but does not waste time in Discussions with the third one because the third is already set to receive a Grant Award. However, if Discussions with the two resulted in increasing the amount of Grant Award to those two and reducing or eliminating the third Applicant, that would be unfair and improper.]] The goal is to improve every Grant Award as to technical merit, capability risk and budget to align as much as practicable with the MCA Entity’s mission, programs and activities.
- Co-Creation Co-Creation occurs when the MCA Entity or its representatives collaborate with Proposers or Applicants or potential Proposers or Applicants in designing Grant Program(s) or developing Concept Note(s), Concept Paper(s) or Application(s). Co-Creation can occur at any stage of the Grant cycle from planning to Grant Award depending upon the Grant Award Procedure being followed. Co-creation is likely to occur with individual Proposers or Applicants but may also be undertaken with a set of Applicants or Proposers. Since Co-Creation can generate innovative development solutions, reduce capability risks, strengthen local ownership and improve sustainability of outcomes, the MCA-Entity is permitted to apply Co-Creation mechanisms as permitted in the Grant Award Procedures. Before engaging in Co-Creation, the MCA Entity must develop a written plan, approved by the MCA Director of Grants. MCC approval would also be required if conditioned in MCC’s approval of a specific Grant Program.
- Screening for Eligibility Requirements regarding the type of entity eligible for funding assistance and the range and scope of eligible Grant Activity will vary among Grant Programs. However, all entities must be screened for eligibility to receive MCC funds per the criteria established in the MCC Program Procurement Guidelines section P1.A.1.7. Accordingly, the MCA Entity must include information on eligibility for types of entities and range of activities in every NOFO, CFCP and RFA. Each Concept Paper, Concept Note and Application will be screened by the MCA Director of Grants for eligibility before it is reviewed for other criteria. The MCA Entity will return the Concept Paper, Concept Note or Application, as relevant, without further review if the Proposer or Applicant fails to satisfy the eligibility requirements before the deadline for submission of the document. The determination that a Proposer or Applicant or a proposed Grant Activity is ineligible is an objective finding made by the MCA Director of Grants whose decision is final.
- Merit Review
The primary purpose of a Merit Review is to provide an independent assessment of the technical merit of an application for financial assistance. Merit Review is the thoughtful, consistent, objective, review and analysis of the technical merit of a Concept Paper, Concept Note, or Application based upon pre-established criteria by persons who are independent of those entities submitting the Concept Papers, Concept Notes or Applications and who are knowledgeable in the fields related to the subject matter of the Grant Activities and the pre-determined criteria. The focus is on analyzing the technical features of what the Proposer or Applicant proposes to do with the funding assistance and not on evaluating the capability risk of the Proposer or Applicant.Merit Reviews may be designed and completed in various formats. There is no uniform list of Merit Review criteria. Rather, the MCA Entity must customize the criteria for review given the particulars of a Grant Program. Moreover, the specific Merit Review criteria must be established before the Grant opportunity is announced and each criterion must be stated in the notice document (CFCP, RFA, and NOFO).The notice document must also identify the relative importance of each criterion. This may be indicated by listing the criteria in order of importance, by stating that all criteria are of equal importance or by providing a numerical or adjectival weight to each criterion. To ensure and preserve transparency and fairness of the process, the Merit Review must be conducted strictly in accordance with the pre-established and announced criteria and ranking system. Thoughtful planning is critical as the criteria and ranking cannot be changed after receipt of the responses to the notice. Each Concept Paper, Concept Note, and Application will be reviewed and analyzed according to the degree to which each satisfies the Merit Review criteria as announced.Merit Review Panel
The Merit Review must be conducted by the Merit Review Panel that has been approved by the MCA Director of Grants. MCC approval of members of Merit Review Panel may be required on case by case basis as determined by MCC. The members of the Merit Review Panel must be free of conflicts of interest with Proposers and Applicants. If qualified, the members of the Merit Review Panel may be the same as the Selection Committee. The members of the panel also must be well qualified, by training or experience or both, in the technical fields that are the subject of the Grant Program, the technical criteria to be applied and the submissions being reviewed. Recognizing that the required knowledge to conduct the review may cut across several fields of expertise, the members of Merit Review Panel, when taken together as a team, must possess all of the technical capability necessary to apply all of the specific Merit Review criteria in reviewing and analyzing the particular Concept Paper, Concept Note, or Application. Each member of a Merit Review Panel must sign a Certificate of Confidentiality and Impartiality, including a statement that any actual, potential, or perceived conflicts of interest will be disclosed to the MCA Entity’s legal advisor, before reviewing the Concept Paper, Concept Note or Application documents.
Merit Review Process The MCA Entity determines the rating system and method that the Merit Review Panel will use in reviewing and evaluating the submissions. The rating system may be adjectival or numeric and the rating method may be consensus or individual. The consensus method represents the collective opinion of all members of the Merit Review Panel. Generally, this method is preferred. However, when the panel is composed of experts representing different highly specialized fields reflecting the diverse and highly specialized nature of the criteria, the individual panel members may be instructed to focus on the evaluation in his or her area of expertise and develop the corresponding supporting narrative critique of strengths and weakness.
In conducting the review, the Merit Review Panel may request additional information from the Proposer or Applicant. The request must be made in writing by the MCA Director of Grants. The request must state a reasonable deadline for response by the Proposer or Applicant which can be extended at the sole discretion of the MCA Director of Grants. If the Proposer or Applicant fails to respond, the MCA Entity may proceed with the review based upon the information before it or may reject the submission.
Merit Review Advisory Report The Merit Review Panel must prepare a Merit Review Advisory Report. This is a written report, signed by each member of the Merit Review Panel, documenting its review and analysis of the submissions. The Merit Review Advisory Report is a critical document within the Application Appraisal Report that is submitted to the Selection Committee. The Merit Review Advisory Report must provide a narrative critique explaining the strength and weakness of each Concept Paper, Concept Note, or Application with respect to each of the pre-established and announced criteria. The Merit Review Advisory Report may also include either numerical or adjectival scores or scores determined by some other methodology and may include recommendations, but these scores and recommendations are for information only and are not binding on the Selection Committee. In the case of Applications, the Selection Committee may, at its discretion, reject an Application based upon the results of the Merit Review without further consideration of the Application. The reasons for rejection must be explained in the Selection Committee Report.
The Merit Review is a key part of the Application Appraisal Report which at minimum includes: 1) the Merit Review Advisory Report, 2) the Capability Risk Assessment Report and 3) the Grant Budget Assessment. This report is given to the Selection Committee which issues a Selection Committee Grant Award Report.
- Capability Risk Assessment
The MCA Entity must assess the probability that an Applicant will successfully carry out a proposed Grant. This examination is distinct from the screening for eligibility and the Merit Review analysis. Rather, this assessment focuses on the potential Grantee and its ability to carry out the proposed Grant Activity.This capability analysis differs from the definitive capacity/qualification determination required under the Program Procurement Guidelines. The procurement procedures limit contract awards only to qualified and capable suppliers and contractors that have the capacity and willingness to perform the contracts. Under Grant Programs, the MCA Entity may award a Grant to a potential Grantee whose ability to carry out the Grant is somewhat questionable. Consequently, the MCA Entity must determine the level of capability risk tolerance for each Applicant whose Application was not rejected after the screening for eligibility or after the Merit Review. The MCA Entity at its discretion may reject any Application if the Capability Risk Assessment results in a finding that there is a substantial risk that the Applicant will not be able to carry out the Grant in compliance with the terms and conditions of the proposed Grant Agreement. The reasons for rejection must be explained in the relevant Selection Committee report.Scope of Capability Risk Assessment
When conducting the Capability Risk Assessment, the MCA Entity must assess all aspects of the potential Grantee’s organization and resources that are relevant to carry out the proposed Grant Activities. These may include, but are not limited to, assessment of financial resources, amount and complexity of prior grants or other funding sources, necessary equipment and facilities, relevant technical resources including ability to comply with environmental and social requirements of the Grant[[See MCC Environmental Guidelines, August 26, 2010 as may be amended from time to time.]], organizational and management structure and experience, accounting and operational controls, procedures for procurement and Subawards, record of past performance in carrying out other grants, record of integrity and business ethics.Process of Capability Risk Assessment
This assessment is conducted under the supervision of the MCA Director of Grants by persons knowledgeable in the elements of the assessment. The assessment may be carried out by MCA Staff, or parties contracted by the MCA Entity for this purpose. Persons serving as members of the Merit Review Panel may also participate in this assessment if qualified. may consider the information submitted in the Application as well as other publicly available information. It may conduct a site visit to local organizations to meet with key staff members and obtain further data on technical, organizational, and financial questions. It may also request additional information from the Applicant. The request must be made in writing by the MCA Director of Grants. The request must state a reasonable deadline for response by the Applicant which can be extended at the sole discretion of the MCA Director of Grants. If the Applicant fails to respond, the MCA Entity may proceed with the assessment or may reject the submission.
Capability Assessment Report The Capability Risk Assessment must result in a Capability Risk Assessment Report which describes the process and the findings of the Capability Risk Assessment. The Capability Risk Assessment Report becomes part of the overall Application Appraisal Report. The Capability Risk Assessment Report must assign a risk level with rationale for each element examined and, if possible, recommend mitigation measures that could be taken to reduce the risk.
- Grant Budget and Grant Budget Narrative
The MCA Entity must include a form for the Grant Budget with the Grant Budget Narrative in every request to submit Grant Applications. Every Grant Application must include a Grant Budget with the Grant Budget Narrative following the prescribed format. While the total Grant Budget amount is never a scored factor for selecting a Grantee, the MCA Entity must review every Grant Budget for cost allowability, allocability, reasonableness and adherence to other cost principles per the MCC Cost Principles for Government Affiliates.Grant Budgets can be denominated in either United States dollars, the local currency of the country of the MCA Entity, or, if justified by sound reason, a combination of the two. The currency of payment must be fixed at the date of the signing of the Grant and changes in the currency of payment after Grant Award are prohibited.The MCA Director of Grants is responsible for ensuring review of the Grant Budget which may be conducted by the Merit Review panel if qualified. The MCA Entity may also request additional information from the Applicant. The request must be made in writing by the MCA Director of Grants. The request must state a reasonable deadline for response by the Applicant which can be extended at the sole discretion of the MCA Director of Grants. The Application Appraisal Report must detail the review of the Grant Budget (Grant Budget Assessment) and must be submitted to the Selection Committee. The amount, terms and conditions of the Grant Budget will be subject to negotiation before Grant Award. The MCA Entity may withdraw a Proposed Grant Award if the Applicant and MCA Entity are unable to agree to the final terms of the Grant Budget.While the prescribed format of the Grant Budget with the Grant Budget Narrative will vary depending upon the Grant Program, the following principles apply to all Grant Budgets as relevant:
- Cost Principles: MCC’s Cost Principles for Government Affiliates must apply to all Grant Budgets and disbursements.
- Unallowable Costs:
Grant Budget may not include funding for unallowable costs. Unallowable costs include, but are not limited to:
- Any funds provided to the military, law enforcement as well as for surveillance equipment;
- Entertainment expenses and promotional items and memorabilia, including models, gifts and souvenirs, as well as advertising and public relations costs designed primarily to promote the Grantee rather than complete the Project;
- Gifts, gratuities, donations;
- Alcoholic beverages and tobacco products;
- Costs incurred before execution of the Grant Agreement;
- Fines, debts and penalties or debts; these remain the sole responsibility of the Grantee;
- Grant-funded air travel in anything other than economy class;
- Promotional items without a clear functional benefit to the Grant Program as that is clearly identified in the Grant Budget Narrative and approved by the MCA Entity;
- Salary or honoraria payments for current government employees;
- Payments of any kind to politically affiliated organizations or parties;
- Direct tax payments or indirect support of Grantee’s tax liability as outlined in the Compact;
- Miscellaneous, undefined and/or contingency costs;
- Compensation of any sort to members of the media for services;
- Speakers fees, stipends and other allowances for persons acting in their official capacity on behalf of the Grantee;
- Costs of any illegal activity contrary to local, provincial or national laws, as well as any prohibited activities under the Compact;
- Unreasonable salary payments and/or any compensation or distribution of Grant funds to officers, staff or shareholders which is not supported by wage reports and employee time sheets for work completed in connection with the Grant;
- Costs of advertising that are not necessary for carrying out the Grant Activities, including advertising and public relations designed to promote the Grantee’s organization;
- Grantees cannot realize a profit or financial gain above its actual cost.
- Cost Share and Leverage: Cost sharing or matching refers to the resources a recipient contributes as a percentage of the partner share, as opposed to the total value of the award. When an individual Grant Program mandates a Cost Share, the requirement must be uniformly and fairly applied. If Cost Share is required for a specific Grant Program, it should be based upon the needs or purpose of the Grant Program and the MCA Entity must document the rationale for this determination. The terms and conditions of a Cost Share requirement must be described in the notice document and accounted for in the Grant Budget. The MCA Entity may reject, at its discretion, an Application without further review if the Cost Share elements of the Grant Budget are substantially inconsistent with the terms set out in the notice document. The Cost Share amount becomes a condition of the Grant Agreement, is verifiable from the Recipient’s records, and may be audited. The Grant Agreement must provide remedies for the MCA Entity if the Grantee fails to meet its Cost Share requirement. Remedies may include, but are not limited to, reduction in the amount of Grant funds disbursed to the Grantee and suspension or termination of the Grant Agreement.An MCC-funded Grant Program may also include Leverage. Leverage means using available resources that a Grantee brings to a Partnership or Grant to obtain additional resources, the Grant, to achieve a total effect that is greater than the sum of the parts. Leverage may be in a variety of forms - anything of value that is measurable such as financial contributions, third party contributions, donated services or property, or intellectual property. Unlike Cost Share, Leverage is not audited and is not part of the budget in the Grant Agreement.
- Milestone Disbursement Schedule:
If the Grant includes funding support in cash, the Grant Budget must include a Milestone Disbursement Schedule. Milestones should be results-based and must represent a clear achievement toward the overall program goals. The Milestone Disbursement Schedule is a projected disbursement schedule tied to defined milestones either in terms of carrying out Grant Activities, results achieved, or costs incurred. Generally, the disbursement is made after the milestone is realized.Because advance disbursements are made before the MCA receives any value for the funds, advance disbursements are not permitted.The following milestone disbursement methods are permitted.
- Progress Disbursement: Disbursement for progress provides funds to the Grantee for making progress on achieving a deliverable, result or outcome. The amount of funds for achieving progress may be based on actual costs incurred, actual percentage of completion or actual stage of completion achieved. Progress payments do not have to equal the costs incurred for creating the relevant deliverable/output and could be in excess of the costs incurred as a means to creating cash flow for attainment of future milestones. This disbursement type is appropriate when the Grant supports a major deliverable, result or outcome with a series of linked actions and costs leading to their realization. An initial progress payment may be made on the submission of a mobilization report, inception report or workplan.
- Performance-Based Disbursement: Disbursement for performance provides funds to the Grantee for actual achievement of a deliverable, result or outcome that represents completed performance of the Grant or an identifiable part of the Grant and gives value to the MCA Entity. This disbursement method is preferred.
- Review for Reasonableness and Cost Efficiency: The Grant Budget must be reviewed for reasonableness, cost efficiency, and compliance with the MCC Cost Principles for Government Affiliates. This includes an analysis of the reasonableness of the proposed budget: appropriateness and reasonableness of resources, reasonableness and feasibility of the Milestone Disbursement Schedule, reasonable alignment of scope, schedule and price or cost. While this review is not scored, no costs above what is reasonable are allowed regardless of the merits of the Application and the capacity of the Applicant. This analysis is documented in the Grant Budget Assessment Report, which becomes a critical document in the Application Appraisal Report and the findings are considered by the Selection Committee in making its decisions regarding Proposed Grant Award.
- Grant Program Policy Factors Grant Program Policy Factors are factors that, while not indicators of the merit of an Application or capability of an Applicant are essential to the process of choosing which Applications and Applicants, individually or collectively, will best achieve the Grant Program objectives. For example, Grant Program Policy Factors may reflect the desirability of selecting Grantees based upon geographic distribution, diverse approaches, or complementary efforts. Such factors must be specified in the notice document inviting submissions to alert Proposers and Applicants that policy factors essentially beyond their control will weigh into the Grant selection process. The Grant Program Policy Factors are not point scored, but the Selection Committee may consider these factors in making the selection for Proposed Grant Award, if the factors were previously announced.
- Selection CommitteeConfirm Selection Committee
Subject to MCC approval, the MCA Entity must appoint a Selection Committee of at least three individuals (but not more than seven for each Grant Program). These individuals may be the same as Merit Review Panel, or the MCA Grants Director may adjust the panel to add or subtract expertise as needed. Each member of the Selection Committee must sign a Certificate of Confidentiality and Impartiality, including a statement that any actual, potential, or perceived conflicts of interest will be disclosed to the MCA Entity’s legal advisor.
Selection Committee Review
Under the two-step Grant Award Procedures, the Selection Committee will initially review the Concept Paper Appraisal Report or the Concept Note Appraisal Report, as relevant, and determine which Proposers are to be invited to submit Applications. These determinations are documented in a Selection Committee Concept Selection Reports.
Under all Grant Award Procedures, the Selection Committee must consider the Application Appraisal Report (which at a minimum includes the Merit Review Advisory Report, the Capability Risk Assessment Report and the Grant Budget Assessment Report). Considering the information and recommendations in the record before it, plus any previously announced Grant Program Policy Factors, the Selection Committee determines which Applicants are proposed for Grant Award weighing the benefits of the technical merits against the level of capability risk, the amount of the award and program policy considerations. In making its award decision the Selection Committee must also provide instructions for negotiating the Grant Agreement including the type of Grant Agreement and any special conditions. These determinations are documented in a final Selection Committee Grant Award Report.
The MCA Director of Grants is responsible for coordinating the Selection Committee, setting timelines, and ensuring that the Selection Committee has the information necessary for its review including the Grant Program description, the notice documents and the appropriate appraisal reports.
Selection Committee Reports and Amendments
The Selection Committee will issue a Selection Committee Concept Selection Report when it determines which Proposers are to be invited to submit Applications and will issue a Selection Committee Grant Award Report documenting its selection of Proposed Grant Awards. Under both circumstances, the reports must provide a record of the Selection Committee’s decisions and recommendation with justification regarding every Proposer or Applicant including those rejected and those not invited to submit an Application or those not chosen for a Grant award. The MCA Director of Grants must ensure that the Selection Committee Concept Selection Reports and the Selection Committee Grant Award Reports include all the necessary documents and that the record of the decisions and recommendations of the Selection Committee is accurate and complete. The Selection Committee Concept Selection Reports and the Selection Committee Grant Award Reports must be signed by the members of the Selection Committee and by the MCA Director of Grants and must be approved by MCC. Any subsequent amendments to these reports must be signed by the members of the Selection Committee and by the MCA Director of Grants. Amendments must be approved by MCC only if the amendment deletes or adds a Proposer or Applicant or if the amendment or cumulative amendments to the Selection Committee Grant Award Reports increase or decrease a proposed Grant amount by more than 10 percent.
- Debriefing The MCA Entity must provide a debriefing upon request to any entity submitting a Concept Paper, Concept Note, or Application that was rejected or denied. The right to a debriefing does not apply to any proposed Sub-recipient. The debriefing is intended to help the entity gain a better understanding of the decision not to proceed with an award of funding assistance with a view to helping the entity improve. A Proposer or Applicant has 10 calendar days to request a debriefing after receiving notice of rejection or denial. The debriefing must be led by the MCA Director of Grants.
- Publication of Grant Awards Within 30 calendar days of signing a Grant Agreement, the MCA Entity must post the notice of Grant Award on the MCA Entity’s website. The notice must identity the Grant Program, the Grantee, the amount of the Grant, and the duration of the Grant. The posting must be in English and in the local language of the MCA Entity’s website, when applicable.
PART 4: Grant Procedures
Grant Award Procedures
Grant Award Procedures: choice begins with key fact-based decisions

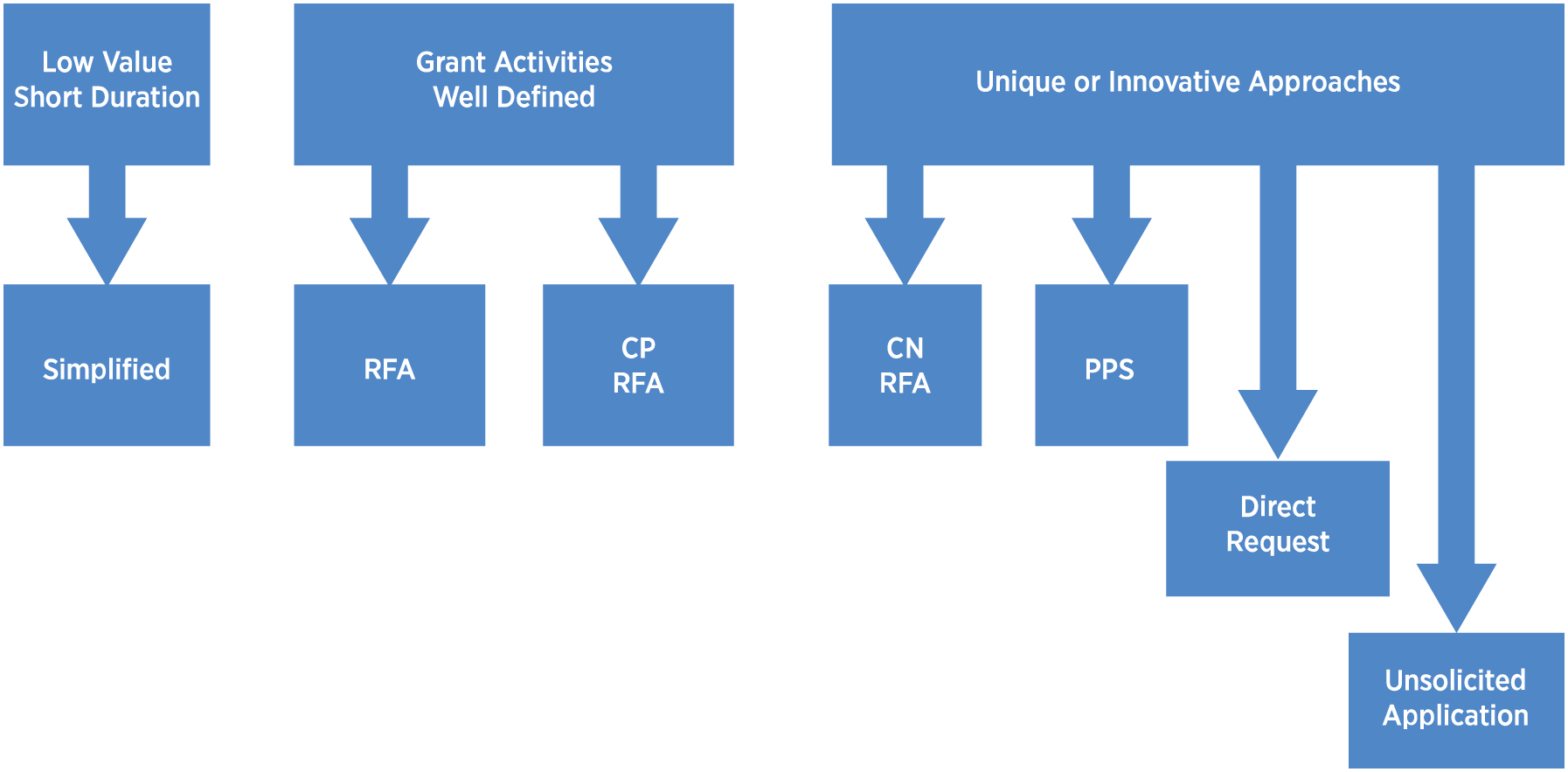
Simplified Procedures: Grants of Low Value and Short Duration
- Grant Award using Simplified Grants with and without Discussions
- Conditions for Use: Simplified Grant procedures are used when the Grant amount to any Grantee under a Grant Program is limited to a relatively low value ($150,000 or less) and is of a short duration, no longer than 12 calendar months. The proposed Grant Activities are usually well-defined in the RFA, but the RFA may request creative approaches to achieve defined results. The terms of award may be an In-kind Grant, a Fixed Amount Grant or a Fixed Amount Grant with Reimbursement for Direct Cost. Reimbursement of indirect costs is never permitted.
- Use of Co-Creation and Discussions: Co-Creation may be used at the planning stage but not during the selection process. Discussions may be used to address capability and budget issues when most of the Applicants are rated at high capability risk. Discussions, in this circumstance, focus on measures to mitigate high risk to enable the MCA Entity to make Grant Awards and implement a Grant Program.
Routine Procedures: Grant Activities are Well-Defined
- Grant Award using One-Step RFA with and without Discussions
- Conditions for Use: One-Step RFA procedure is used when (i) the Grant Activities can be well-defined, (ii) the general approach to carry out the Grant is either straight forward or also well-defined, and (iii) the information the MCA Entity needs to assess the potential Grantee’s ability to carry out the Grant Activities can be uniformly and clearly described. Since this procedure is used for Grant Awards above $150,000, the documents are more detailed and complex than used for Simplified Grants. This procedure may be used for a Grant Program in which multiple awards are envisioned.
- Use of Co-Creation and Discussions: Co-creation may be used at the planning stage to develop Grant Activities. At the Grant Award stage, Co-Creation may be used for building capability including ways the Grant may be governed.Discussions, if needed, can focus around capability of the Applicant or budget issues but should not be used to develop Grant Activities.
- Grant Award using Two-Step Concept Paper/RFA with and without Discussions
- Conditions for Use: Like the One-Step RFA procedure, this procedure is used for Grant Awards when (i) the Grant Activities can be well-defined, (ii) the general approach to carry out the Grant is either straight forward or also well-defined, and (iii) the information it needs to assess the potential Grantee’s ability to carry out the Grant can be uniformly and clearly described. The decision to begin the process by requesting Concept Papers rests with the MCA Entity and could be based upon contrasting circumstances. Since a Concept Paper takes less time to prepare than an Application, requesting Concept Papers might be preferred when the MCA Entity is looking to encourage greater interest in the funding assistance opportunity. Alternatively, the MCA Entity might believe that interest in the funding is so great that the burden of reviewing Applications could be reduced by first screening Concept Papers. The MCA Entity might also prefer to begin the process with Concept Papers to refine the information and descriptions in the RFA before asking for Applications.
- Use of Co-Creation and Discussions: Co-Creation may be used as per the One Step RFA.Discussions, if needed, can focus around capability or budget issues but should not be used to develop Grant Activities.
Exceptional Procedures: Unique or Innovative Activities and Approaches
- Grant Award using Two-Step Concept Note/RFA with and without Discussions
- Conditions for Use: This procedure is used when the MCA Entity has a well-defined Grant Program, but the MCA Entity is seeking creative approaches for Grant Activities or innovative ways to carry out Grant Activities, or both. This procedure is particularly well suited for seeking to make large, complex Grants or awarding multiple large Grants under a single Grant Program.
- Use of Co-Creation and Discussions Co-Creation may occur during planning or at any stage of this procedure and may be especially useful in preparing Applications after screening the Concept Notes.Although the MCA Entity may apply this procedure without Discussions, this tool can be particularly useful in conducting these procedures and would be undertaken frequently when using this procedure to make Grant Award decisions.
- Program Partnership Solicitation
- Conditions for Use The Program Partnership Solicitation leading to Cooperation Agreement is used when the MCA Entity determines that a significant level of cooperation is warranted for the design and implementation of approaches or methodologies to achieve a Compact objective and the requirements of Program Partnership are appropriate. Program Partnership seeks program Cost Share of no less than 25 percent when feasible and warranted, with higher levels of Cost Share generally preferred. The Grant governance benefits from a Partnership Advisory Committee to include members—beyond MCA Entity and the Grantee—who are authorized to provide guidance to mobilize expertise or other resources for the activity, and to provide advice on the adaptation of the joint effort for successful outcomes. A two-step procedure for Grant Award is used.
- Use of Co-Creation and Discussions: Co-Creation is always used for this procedure. Discussions are permitted at any stage in the Grant Award process.
- Grant Award based upon Direct Request
- Conditions for Use This Direct Request procedure for Grant Award is permitted only in exceptional circumstances when the entity has been determined to be the only entity that can perform the Grant Activities either because of its unique mission, programs and activities and because there is a unique circumstance that would limit the ability of any other potential Grantee to carry out the Grant Activities. Since an open, competitive process is not being followed, the use of Grant Award based upon Direct Request must be approved by MCC and the written justification along with MCC’s approval must be maintained in the Grant file.
- Use of Co-Creation or Discussions Co-Creation and/or Discussions may occur at any time during the Grant Award process.
- Grant Award based upon Unsolicited Application
- Conditions for Use While Unsolicited Applications can be received and reviewed for funding, Grant Awards to the Applicant will be made only in highly exceptional circumstances and only with the approval of MCC. To be considered, an Unsolicited Application must be extraordinary. It must reflect unique technical merit that is consistent with the objectives of the Compact and must be submitted by an eligible Applicant that demonstrates unique capability with extremely low capability risk.
- Use of Co-Creation and Discussions: Co-Creation is inconsistent with the conditions of use for this procedure.Discussions are permitted for any aspect of the Application.
Negotiation of Grant Agreements
Grant AgreementsFollowing the award decisions and instructions of the Selection Committee, the MCA Director of Grants must organize the negotiations of Grant Agreements with the proposed Grantees. The negotiations should focus on the terms of the Grant Agreements. These Grant Guidelines in provide considerable flexibility for defining the Grant relationship in Grant Agreements. The disbursement arrangements and the terms and conditions of each Grant Agreement will be determined as appropriate to meet the particulars of the Grant Activities, the capability of the potential Grantee and the form and details of the Grant Budget. Within one Grant Program, the disbursement type and the terms and conditions of each Grant Agreement may differ depending upon the particulars of each Grant and potential Grantee. However, it is important that the MCA Entity adhere to the principle of fairness between and among the potential Grantees when negotiating multiple Grant Agreements. If the potential Grantee and the MCA Entity are unable to come to agreement on the type, terms and conditions of the Grant Agreement, the Proposed Grant Award is canceled.
Memorandum of Negotiation
The MCA Director of Grants must prepare a “Memorandum of Negotiation” if during negotiations the Selection Committee agrees to accept changes to the terms and conditions of the Grant Agreement from the original instructions of the Selection Committee as set out in the Selection Committee Grant Award Report. This document will be signed by the potential Grantee and the MCA Director of Grants and approved by a representative of the Selection Committee and by MCC. This document must be included in the record of the Grant. The Grant Agreement must set out the order of precedence to ensure clarity of interpretation.
PART 5: Grant Relationships Defined
Types of Grant Relationships
The MCA Entity must determine the appropriate Grant relationship for each Grant depending upon the facts and circumstances of the Grant and the Grantee. Since many of these facts and circumstances are unknown until after review of Grant Applications, the MCA Entity is not required to announce the terms and conditions of future Grant Agreements when announcing the Grant opportunity.The MCA Entity must follow the conditions for using each of the Grant types and certain types may require MCC prior approval as indicated in Attachment A, Program Grant Guidelines Approvals Matrix.
Except for Cooperation Agreements, the choice of Grant relationship can be made at any stage during the Grant formation process. Grant relationships can vary among Grantees under the same Grant Program. In some circumstances the MCA Entity may gain sufficient information about the circumstances of the Grants and potential Grantees during the planning stage to determine the type of Grant relationship to use for every Grant under a particular Grant Program.[[Under these circumstances it is recommended that the MCA Entity include the anticipated form of Grant Agreement in the Grant notice documents.]] In other circumstances the MCA Entity may determine the disbursement mechanism early in the Grant formation process but remain flexible regarding the type of Grant of terms and conditions until reviewing Applications. At the other extreme, the MCA Entity, through the Selection Committee, might condition the proposed award upon successfully negotiating a Grant Agreement that incorporates the Grant types with provisions as dictated in its instructions.
These Grant Guidelines provide several Grant types organized in two categories to be used to develop the Grant relationship for each Grant Agreement. Except for the Cooperation Agreement which defines all elements of the Grant relationship, each Grant Agreement will include at least one Grant type from each category. However, a single Grant Agreement might combine additional clauses from either or both categories. This system provides ample and needed flexibility in defining the Grant relationship.[[Detailed instructions for developing Grant Agreements are set out in the Grants Operations Manual.]]
Category I set out Grant types according to the disbursement mechanism. Four types of Grant disbursement mechanisms are permitted:
- In-Kind Grant
- Fixed Amount Grant
- Fixed Amount Grant with Reimbursement for Direct Costs
- Cost Reimbursement Grant
- Simplified Grant
- Standard Grant
- Grant with Special Conditions
- Grant with Substantial MCA Involvement (Cooperative Agreement)
- Grant with Limited MCA Involvement
- Cooperation Agreement (Program Partnership)
Category I: Disbursement Mechanisms
- In-Kind Grant
- Description: An In-Kind Grant means a Grant in which the MCA Entity supports the Grantee not through direct funding but by procuring the goods and/or services needed to carry out the Grant and then providing them directly to the Grantee. The In-Kind Grant can be the only form of support provided by the MCA Entity to the Grantee or an In-Kind Grant may be incorporated into a Grant Agreement that includes another disbursement mechanism for the Grantee to carry out other Grant Activities.
- Conditions for use:
In-Kind Grants have multiple potential uses. The MCA Entity may use an In-Kind Grant when:
- The MCA Entity determines that a Grantee or class of Grantees are deemed to lack adequate capacity to manage procurement. This determination may be based upon the Capability Risk Assessment of an individual Applicant or the MCA Entity may also design a Grant Program to provide only In-Kind Grants in anticipation that all the potential Grantees will lack capacity in procurement.
- The MCA Entity determines it will be more cost effective or efficient for it to procure the goods, works and/ or services.[[For example, this may occur when the MCA Entity finds after conducting market research that it can realize volume savings if it conducts a single procurement that would serve the needs of several Grantees.]]
- The MCA Entity determines that this type of Grant is desirable because there is an impediment to transfer funds to a Grantee.
- The Grant Activities require an initial large investment in goods, works and/or services and the MCA Entity determines to use this type of Grant as a substitute for a not permitted advance disbursement.
- Fixed Amount Grant
- Description: Fixed Amount Grant is a type of Grant Agreement under which the MCA Entity commits to a specific level of support to the Grantee for carrying out the Grant Activities. This type of Grant relationship reduces some of the administrative burden and reporting requirements for the MCA Entity as Grantor and its Grantee. Because the costs have been determined in advance, accountability is based primarily on performance (subject to performance audits) and results as opposed to reviews of actual costs incurred.The total amount of the Grant is determined at Grant Award. Based upon review of the Grant Budget, the MCA Entity must establish that the fixed amount of award is justified and can be priced with a reasonable degree of certainty and must find there is reasonable assurance that the Grantee will not realize a profit or financial gain above its actual cost.No indirect costs or percentage-based overhead allocations can be incorporated as part of the MCA-funded portion of a Fixed Amount Grant. Cost components to be incurred by the Grantee which can be individually defined and determined to be allocable to the Grant Activities even when shared by other programs may be defined as direct cost and included in the MCA-funded portion of the Grant at the discretion of the MCA Entity if the Grant meets the standard for using a Fixed Amount Grant.
- Conditions for use: A Fixed Amount Grant is used only when the Grant Activities are specific, when expected activities can be reliably predicted, and when the Grant Activities to be carried out can be priced with a reasonable degree of certainty and with reasonable assurance that the Grantee will not be able to realize an increment of profit above its actual cost.
- Fixed Amount Grant with Reimbursement for Direct Costs
- Description: The Fixed Amount Grant with Reimbursement for Direct Costs is a Grant that provides two disbursement mechanisms. The Grant Agreement includes a Milestone Disbursement Schedule for disbursement of the fixed amount portion of the Grant based upon achievement of milestones. Additionally, the Grant Agreement will include a schedule of disbursement for inputs. This provides for the reimbursement of certain actual direct cost when incurred.
- Conditions for use: The Fixed Amount Grant with Reimbursement for Direct Costs may be used instead of the Fixed Amount Grant when it is difficult to estimate the actual cost of certain direct costs.
- Cost Reimbursement Grant
- Description: Under a Cost-Reimbursement Grant, the MCA Entity reimburses the Grantee for reasonable, allocable and allowable costs incurred up to a ceiling amount established in the Grant Agreement. As with other types of Grants, programmatic milestones for disbursement must be established in the Grant Agreement and the milestone completed as detailed in the grant agreement before disbursement is made.
- Conditions for use:
Cost-Reimbursement Grant should be used where the cost to carry out the Grant Activities are unable to be estimated with a reasonable degree of certainty and/or the MCA Entity is unable to establish reasonable assurance that the Grantee will not realize a profit or financial gain above its actual cost.Additionally, a Cost-Reimbursement Grant may be used only when:
- Grantee has an accounting system that is capable of accounting for the funding provided, reporting expenses incurred in connection with the MCA-funded Grant Activities separately from either Grantee Cost Share expenses or other donor programs outside the scope of the MCA Entity Grant. MCC requires the Grantee to maintain a separate bank account for funds under a Cost Reimbursement Grant unless otherwise agreed; and,
- Grantee, as determined by MCA, is capable of submitting its financial statements to a financial audit to the standards of, and when required by, the Guidelines for Financial Audits Contracted by the Millennium Challenge Corporation's Accountable Entities or at the request of MCA or of MCC; and,
- MCA Entity has sufficient resources in place to administer and provide oversight of the Cost Reimbursement Grant.
Category II: Terms and Conditions
The following list of six Grant types begins with the Simplified Grant and then continues with the Standard Grant. Either one will establish the basic Grant relationship that requires the MCA Entity to exercise administrative oversight of the Grantee. The Simplified Grant format gives the MCA Entity the option to use a brief form of Grant Agreement more appropriate to the size and duration of these smaller Grants. The Standard Grant is the starting point for the terms and conditions in all Grants except for Simplified Grants and Cooperation AgreementsAdditionally, the MCA Entity can adapt the Grant relationship to include additional provisions beyond those establishing its standard oversight function. As the name implies, the Grant with Special Conditions provides a means to add special conditions to the Simplified Grant or the Standard Grant which the Grantee must satisfy either before or as it proceeds with carrying out the Grant.
The Grant with Substantial Involvement (Cooperative Agreement) and the Grant with Limited Involvement provide the MCA Entity with two ways to modify the Standard Grant relationship when the MCA Entity determines to collaborate and participate, substantially or partially, in carrying out programmatic aspects of the Grant. Finally, the Cooperation Agreement (Program Partnership) provides and additional relationship characterized by full collaboration between the MCA Entity and its partner Grantee.
- Simplified Grant
- Description: Simplified Grant establishes a Grant relationship of short duration and relatively low value. Appropriately for these circumstances, the MCA Entity may use a short form Grant Agreement setting out the rights and obligations of the parties in clear and precise terms with minimum cross-cutting requirements and responsibilities.
- Conditions for use: Simplified Grant procedures are used for Grants of low value (at or below $150,000) and of short duration (no longer than 12 calendar months).
- Standard Grant
- Description: The Standard Grant establishes the Grant relationship that requires the MCA Entity to conduct administrative oversight to assure that the terms and conditions of the Grant Agreement are met and that the objectives of the Grant are accomplished without any need for special conditions or additional involvement.
- Conditions for Use: The MCA Entity must apply the Standard Grant terms and conditions for all Grants except Simplified Grants. The MCA Entity may supplement the Standard Grant terms and conditions with those described in Grant with Special Conditions and/or Grant with Substantial MCA Involvement (Cooperative Agreement) or Grant with Limited MCA Involvement when the conditions for use of these Grant types are met.
- Grant with Special Conditions
- Description: The MCA Entity may add special conditions to any Grant to address needs that are specific to the proposed Grantee or specific to the Grant Program. Grantee specific conditions are determined during the planning stage or by the Selection Committee. All special conditions must be incorporated into the Grant Agreement and accepted by the Grantee as a condition for award.
- Conditions for use: The MCA Entity may add special conditions to a Grant Agreement to reduce a risk that is identified when assessing the Application. Often this will be a risk in capability of the Grantee, but it might also relate to a technical risk. In such cases the conditions are specific to the Grantee and must be satisfied by the Grantee. If the MCA Entity must apply its resources, beyond merely advice or guidance, to support the Grantee in satisfying the condition, then the MCA Entity should use a Grant with Substantial or Limited Involvement and not a Grant with Special Conditions. The MCA Entity may also add special conditions to a Grant that is a program specific requirement. Such condition or conditions are specific to a Grant Program, usually determined during the planning stage of the Grant Program and incorporated into all Grants awarded under that Grant Program.
- Grant with Substantial MCA Involvement (Cooperative Agreement)
- Description: A Grant with Substantial MCA Involvement means a Grant in which the MCA Entity collaborates and participates in a substantial way in the programmatic aspects of carrying out the Grant on a regular, on-going basis during the entire period of performance of the Grant. Substantial involvement may mean the MCA Entity must approve key personnel, work plans and/or M&E plans. The elements and scope of involvement are not uniform but are determined according to the needs and circumstances of the Grant. The MCA Entity may determine to use a Cooperative Agreement at any stage in the Grant Award process from planning through to negotiation of the Grant Agreement.[[A Grant with Substantial MCA Involvement is not to be confused with Co-Creation. Co-Creation occurs before the Grant Agreement is signed whereas the elements and scope of involvement in a Cooperative Agreement occur after the Grant Agreement is signed.]]
- Conditions for use: A Grant with Substantial Involvement is used when the MCA Entity wants to be involved throughout the duration of the Grant in the actions and decisions of carrying out the Grant. This may be justified as a mitigation measure if the Grantee is high risk yet the MCA desires to make this Grant to realize highly desirable programmatic objectives. Alternatively, use of this type of Grant may be justified when the MCA Entity can anticipate a clear need for it to be involved in decisions during the duration of the Grant. This might occur in a complex Grant that may require redirection or collaborative problem-solving as the Grant implementation unfolds.
- Grant with Limited MCA Involvement
- Description: A Grant with Limited MCA Involvement means a Grant in which the MCA Entity collaborates and participates in certain programmatic aspects of carrying out the Grant in a material way. The elements, scope, areas and period of involvement are not uniform but are determined according to the needs and circumstances of the particular Grant. The MCA Entity may determine to use a Grant with Limited MCA Involvement at any stage in the Grant Award process from planning through to negotiation of the Grant Agreement.
- Conditions for use: A Grant with Limited MCA Involvement is used when the MCA Entity determines that it needs to be involved post-award in a limited way to mitigate a risk or risks that may affect carrying out the Grant successfully. This could be due to the nature of the Grant, such as a Grant that includes construction activities. It also could be used to help mitigate weaknesses specific to the Grantee especially in the areas of compliance with cross-cutting issues such as environmental, social and safety requirements. In contrast to a Grant with Special Conditions, a Grant with Limited MCA Involvement requires the MCA Entity to invest its resources in a way that enhance the capability of the Grantee to carry out the Grant successfully. In contrast to a Grant with Substantial MCA Involvement, under a Grant with MCA Limited Involvement, the MCA Entity will not be substantially involved in carrying out the programmatic aspects of the Grant as a whole but rather will be focusing and limiting its involvement to specific areas, aspects or time period of the Grant Activities.
- Cooperation Agreement (Program Partnership)
- Description: A Cooperation Agreement is a type of Grant used as a legal and disbursement vehicle for a relationship characterized by Co-Creation, Cost-Share, and significant cooperation between an MCA Entity and the Grantee in the realization of the objectives of the Grant Program.
- Conditions for use: A Cooperation Agreement is used when the MCA Entity determines that a significant level of cooperation is warranted for the detailed design of approaches or methodologies to achieve a Compact objective, program Cost Share of no less than 25 percent is feasible and warranted, with higher levels of Cost Share generally preferred, and project governance can benefit from a Partnership Advisory Committee authorized to provide guidance to mobilize expertise or other resources that contribute to successful outcomes and to provide advice on the adaptation of the joint effort for successful outcomes.
PART 6: Grant Management and Administration
Grant Management and Administration
General
The MCA Entity must ensure that the requirements for each MCC-funded Grant are met and that the Grantee complies with terms and conditions of the Grant Agreement, including the financial and programmatic reporting requirements and the environmental and social requirements.Before signing a Grant Agreement, the MCA Entity must have in place sufficient resources and planning for exercising its responsibility to manage and to administer the Grant. This includes oversight of the programmatic aspects of the Grant as well as overseeing the full range of administrative and financial matters. This requires diligent oversight through well-planned and executed site visits, thorough review of programmatic and financial reports, and diligent review of deliverables. The MCA Entity also needs to be prepared to perform or support required financial and programmatic audits.
The MCA Entity’s Grant Managers and Grant Facility Managers who administer and manage Grants must be qualified to perform their duties and responsibilities. Grant Managers and Grant Facility Managers may be hired or procured or a combination of both.
The MCA Entity must ensure that its Grantees understand their roles and responsibilities and the required rules and requirements that govern their Grants. To carry out this responsibility, the MCA Entity may provide post-award workshops and/or instruction materials to Grantees as appropriate to the scope, complexity and duration of each Grant and the capacity of each Grantee.
The MCA Entity also must ensure that its Grantees establish and maintain effective internal controls that provide reasonable assurance that awards are being managed in compliance with the terms and conditions of the Grant Agreement. A basic structure for internal controls should include processes for planning, organizing, directing, controlling, and reporting on the Grantee’s operations to carry out the Grant.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Every Grant Agreement must require the Grantee to track and report data to feed the monitoring and evaluation plan for Compact as required by the MCA Entity. The MCA Entity must verify that the data is accurate and complete and received on time. Failure to submit accurate and complete data on time may be grounds for the MCA Entity to suspend or terminate the Grant.Financial Management and Financial Reporting
Financial Management SystemThe acceptance of a Grant Award creates a legal duty on the part of the Grantee to use the funds available under the Grant in accordance with the terms and conditions of the Grant Agreement. Except for In-kind Grants, every Grant Agreement must require the Grantee to maintain a financial management system that is adequate and sufficiently detailed to track and account for the expenditure of Grant funds and to ensure that such funds are managed responsibly and effectively and in accordance with the terms and conditions of the Grant Agreement. The scope of the Grantee’s financial management system must cover key functions within the Grantee’s organization and, depending upon the type and terms of the Grant, may include internal controls, disbursements, cost-sharing, program income, budget revisions, audits, cost allowability, and financial reporting.
Financial Reporting
The MCA Entity must ensure that the Grant Agreement requires financial reporting appropriate for the size and complexity of the Grant and the capacity of the Grantee. The Grant Agreement must also ensure that the Grantee has an obligation to produce documents at the request of the MCA Entity to verify information set out in the financial reports. The MCA Entity’s Grants Operations Manual must include procedures, based on the type, size, and complexity of the Grants under management, that require the MCA Entity to monitor financial reporting to provide reasonable assurance (i) that the Grantee is incurring costs allowable under the Grant Agreement and allocable to the approved Grant Activities, (ii) that sufficient supporting documentation is being maintained by the Grantee, and (iii) that the Grantee is carrying out the Grant within the limitations defined by terms and conditions of the Grant Agreement including the Grant Budget.
Mismanagement of Grant Funds
The MCA Entity must develop, document, and comply with procedures designed to identify instances of noncompliance with the Grant Agreement and/or mismanagement of Grant funds. The mismanagement of Grant funds includes: (1) use of Grant funds for a purpose other than what has been approved in the Grant Agreement, (2) deficient accounting for Grant funds, or (3) fraud and abuse.
The MCA Entity must stop disbursement of Grant funds, giving written notice to the Grantee, upon evidence of mismanagement of Grant funds until the matter has been investigated and resolved. Any evidence of fraud and abuse must be reported immediately to MCC as per MCC’s AFC policy. The MCA Entity must suspend the Grant if the mismanagement is material. If the matter is not resolved to the satisfaction of the MCA Entity and MCC, the Grant must be terminated, in whole or in part, as appropriate.
Financial Records Maintenance and Financial Audits
Financial RecordsThe MCA Entity must ensure that under the terms of the Grant Agreement the Grantee is held fully responsible for the effective and proper administration of Grant funds. The terms of the Grant Agreement must require the Grantee to maintain books, records, documents and other evidence related to use of Grant funds for a defined period of time.
Financial Audits
The Grant Agreement must give the MCA Entity the right to conduct an audit or financial review of the Grantee at any time for any reason. A financial audit is intended to provide assurance that the Grantee has been timely, accurately and fairly reporting the financial position and results of operations and is using Grant funds in compliance with funding requirements. An audit will review the Grantee’s administration of Grant funds and any required Cost Share to ascertain whether the Grantee has done the following:
- Established an accounting system integrated with adequate internal fiscal and management controls to provide full accountability for revenues, expenditures, assets and liabilities, which will provide reasonable assurance that the Grantee is managing Grant funds in compliance with the terms and conditions of the Grant Agreement.
- Prepared financial statements that are fairly presented and are in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles prescribed in the Compact country or otherwise designated in the Grant Agreement.
- Submitted financial reports that contain accurate and reliable financial data and that comply with the terms of the Grant Agreement.
- Expended the Grant funds in accordance with the terms of the Grant Agreement.
Cost Share
The MCA Entity must undertake monitoring and other reasonable measures to ensure that the Grantee properly fulfills its Cost Share obligations as set out in the Grant Agreement. Cash and in-kind contributions can be acceptable Cost Share under the following conditions:- The contribution needs to be verifiable. The Grantee needs to be able to demonstrate that the contribution was made by supporting evidence in financial records and source documents.
- The contribution must be necessary to carry out the Grant and provided for in the Grant Budget.
- The contribution must be allowable under the MCC Cost Principles.
- The valuation of in-kind contributions must be reasonable.
- The same contribution cannot be included as a contribution in another MCA Entity Grant.
Programmatic Records and Programmatic Reporting
Programmatic RecordsAll Grant Agreements must require the Grantee to maintain programmatic records connected with the management of the Grant including the backup materials and source documents for programmatic reports and to retain the records for a defined time period. The programmatic records and reports track its progress in carrying out the Grant Activity and include property records, procurement records, Subaward records and records of its compliance with environmental and social requirements.
Programmatic Reporting Requirements
All Grant Agreements must contain provisions for periodic reporting on the progress and results of Grant Activity by the Grantee. In setting the reporting requirements, the MCA Entity must consider the following factors: (1) amount and duration of the Grant; (2) the complexity of the Grant Activity; (3) the Capability Risk Assessment of the Grantee; (4) the schedule of deliverables; and, (5) the Milestone Disbursement Schedule; and (6) information that the MCA Entity is required to provide to MCC.
Recipients of Simplified Grants must be required to submit reports no less frequently than monthly as specified in the Grant Agreement.
The MCA Entity’s Grants Operations Manual must include procedures, based on the type, size, and complexity of the Grants under management, that require the MCA Entity to monitor programmatic reporting in order to determine if milestones and other conditions to Grant disbursements are met prior to disbursement being authorized. These procedures should include programmatic oversight procedures designed to validate and verify the reporting provided, consistent with a risk-based assessment of the Grant Program and Grant Activities being administered by the MCA Entity, with a focus on physical validation of milestone achievement and Grantee’s results in the field.
Final Report
All Grant Agreements must require the Grantee to submit a final completion report that compares the final achievements with the original objectives, describes the reasons for any deviations and explains any obstacles that were overcome as the Grantee was carrying out the Grant. Grant Agreements providing for in-cash disbursement must require that the final disbursement must not be made until all reporting requirements are satisfied.
Procurement by Grantee
The MCA Entity must not allow a Grantee to conduct the procurement of goods, works or services to carry out a Grant unless the MCA has determined through the Capability Risk Assessment that the Grantee has a procurement system that follows the principles of the Program Procurement Guidelines (open, transparent, based on competition with only a commercially reasonable price paid) and that the Grantee has the capacity to conduct procurement in compliance with these standards[[Please see the Program Grants Operating Manual for further guidance on assessing Grantee procurement systems.]]. MCC may request approval and review of a Grantee’s procurement system before allowing the Grantee to make purchases.Subawards
The MCA Entity must not allow a Grantee to make Subawards except under the following conditions:- The MCA Entity must approve a written justification explaining why a procurement contract is not the correct legal instrument and documenting the Grantee’s intent to benefit a Sub-recipient who shares the mission, programs and activities aligned with the Grantee’s to achieve the public purpose objective. This justification may be included in the Grant Application.
- A Subaward agreement that passes through all or most of the key responsibilities to carry out the Grant requires the MCA Entity and MCC prior approval. The Sub-recipient must meet all the eligibility requirements for award of the Grant, be chosen in a competitive process, and its Capability Risk Assessment must be equal to or lower risk than the Grantee. The request for approval must also describe the Grantee’s plan and resources to oversee and manage the Sub-recipient in carrying out the Grant Activities.
- A Subaward agreement under which the Sub-recipient joins with the Grantee in carrying out the Grant requires the MCA Entity prior approval. If the Grant Agreement (including the approved Grant Budget) did not provide that the Grantee planned to carry out the Grant in conjunction with a Sub-recipient, MCC prior approval is also required. A request for approval by the MCA Entity and MCC must describe the scope, range and value of Grant Activities that the Sub-recipient will carry out, the method of selection of the Sub-recipient, and the Grantee’s plan and resources to oversee and manage the Sub-recipient in carrying out the Grant Activities. If the Subaward agreement plan and Sub-recipients are approved during the Grant Award process, additional approval by the MCA Entity is not required.
Asset Management
EquipmentMCC Grant funds may be used to purchase eligible equipment if the equipment is necessary to carry out the Grant and are approved as part of the Grant Agreement. Equipment means tangible personal property having a useful life of more than one year and a per unit acquisition cost of the equivalent of 5,000USD or more, at the exchange rate (as specified in the Grants Operations Manual) on the date of acquisition. MCC Grant funds must not be used to purchase equipment related to the prohibitions specified in Section P2.1.2.3: Ineligible Activities.
The MCA Entity must ensure that the Grant Agreement provides that title to the equipment purchased with Grant funds vests with the MCA Entity until such time as the MCA Entity transfers title to the Grantee or another beneficiary. As with any Program Asset of the Compact, the determination of the final beneficiary of equipment purchased through a Grant Agreement is based on a demonstrated need and the willingness and ability to further the Compact objectives and sustain the Compact results. In any Grant Agreement, the MCA Entity should consider whether the Grantee is the certain or likely beneficiary and clearly address this issue in the Grant Agreement. If the Grant Agreement includes provisions for transferring title of the equipment to the Grantee prior to Compact End Date, this transfer shall be subject to the following conditions in addition to any conditions specific to the Grant Program. The Grantee (1) cannot encumber title, (2) must keep the property insured, (3) must keep the property maintained according to an adequate maintenance plan, and (4) must use the property solely to carry out the Grant during the term of the Grant unless the Grant Agreement specifically permits limited and incidental use of the property for other aligned purposes.
The Grant Agreement should also provide that the Grantee will notify the MCA Entity and request disposition instructions if the Grantee has no use of the equipment to carry out the Grant before the end date of the Grant.
The MCA Entity must monitor the Grantee’s compliance with the conditions of title of MCC funded equipment.
Supplies
Grant funds may be used to purchase eligible supplies if the supplies are necessary to carry out the Grant and are approved as part of the Grant Agreement. Supplies mean tangible personal property that is not deemed equipment and has an acquisition cost of less than 5,000 United States dollars at the exchange rate (as specified in the Grants Operations Manual) on the date of acquisition regardless of useful life.
The MCA Entity must ensure that the Grant Agreement provides that title to the supplies purchased with Grant funds vests with the Grantee subject to the condition that the Grant funded supplies are used solely to carry out the Grant and that the Grantee maintains adequate internal controls to substantiate that the supplies are used for Grant purposes.
Intangible Property
MCC Grant funds may be used to purchase or develop intangible property. This is generally in the form of intellectual property but could include any form of intangible property. The MCA Entity must ensure that the Grant Agreement provides for title of intangible property purchased or developed with Grant funds to vest with the Grantee. The Grant Agreement must also provide that the Grantee must grant a royalty-free, nonexclusive, irrevocable, paid-up license without geographic limitation to the MCA Entity in any intellectual property developed by the Grantee with Grant funds.
Grant Modifications
Decisions pertaining to changes and modifications of Grant Agreements are within the discretion of the MCA Entity. The Grantee has no right to compel any changes or modifications. The following is a non-exhaustive list of rules for modifications that may be made by the MCA Entity.-
- Change of Grantee
Generally, a Grant is not assignable by the Grantee to another entity. If a Grantee is unable to implement the Grant Activities as originally contemplated, the Grant should be terminated. An alternative Grantee may be designated after the expiration date of the Grant only if the alternative Grantee:
-
-
- shares the same mission, programs and activities,
- is continuing the same Grant Activities for the same purpose as the original award,
- is serving substantially the same beneficiary community, and
- is determined to be a low risk in a Capability Risk Assessment.
-
Name change or takeover
If a Grantee changes its name or is assumed by a new organization without disturbing the rights and obligations of the Grantee under the Grant Agreement, the MCA Entity may modify the Grant Agreement as an administrative action without prior approval of MCC. The MCA Entity must give MCC notice of the name change and maintain a clear record of the modification of the Grant Agreement in the Grant file.
- Increase in beneficiary community If a Grant to achieve an outcome or target defines a number of beneficiaries, the MCA Entity may amend the Grant to enlarge the population of the beneficiary community to be served in order to achieve the outcome or target. The MCA Entity must seek and receive MCC approval before modifying a Grant to materially increase (more than 10 percent) the beneficiary community.
- Time or period extension without additional funding (no-cost extension) The MCA Entity may modify the time schedule for achieving milestones or deliverables during the period of the Grant or extend the Grant beyond the original expiration date if the conditions affecting the ability of the Grantee to meet the milestones change for reasons that were reasonably unforeseeable and beyond the control of the Grantee or if the MCA Entity otherwise reasonably determines that changed circumstances fully justify a change in the time schedule or extension of the original expiration date. MCC approval is required for any time extension of 25 percent or more to the original Grant. The amended schedule and any extensions must be consistent with the programmatic objectives within the period for implementing the Compact; otherwise the MCA Entity may terminate the Grant.
- Realignment of Milestone Disbursement Schedule without additional funding Any modification of disbursement amounts between milestones must be fully justified. Any transfer of funds between milestones that exceeds 25 percent of the total amount of the Grant requires MCC’s prior approval.
- Increasing amount of Grant or Grant ceiling Except in the case of In-kind Grants, increasing the amount of Grant award or Grant ceiling without an increase in Grant Activity or deliverables is generally prohibited. MCC’s prior approval is required and will be given only in highly exceptional circumstances and upon evidence that providing additional funding support to the Grantee is essential to realize key programmatic results.
- In-Kind Grant - change in funding Should the actual cost of the goods and/or services vary from the estimated cost in the Grant Budget, the MCA Entity may modify the Grant Agreement to increase or decrease funding as appropriate. A modification to increase the funding by more than 20 percent requires MCC’s prior approval. Alternatively, if the budget is insufficient to cover the goods and/or services, the MCA Entity may give the Grantee the option to contribute the additional funds; or, it may cancel the procurement(s) and terminate the Grant; or, it may seek to modify the Grant Activities.
- Fixed Amount Grant - reduction in Grant Activities or deliverables The MCA Entity cannot modify the Grant Agreement to reduce the Grant Activities or deliverables without a corresponding reduction of the Fixed Amount of the Grant unless approved by MCC. Significant reduction in the inputs including changes to key personnel or significant reduction in level of time commitment could result in an amendment to the Grant Agreement reducing the level of funding support committed by the MCA Entity.
- Fixed Amount Grant with Reimbursement of Direct Costs - reduction in Grant Activities or deliverables The MCA Entity cannot modify the Grant Agreement to reduce the Grant Activities or deliverables without a corresponding reduction of the Fixed Amount portion of the Grant Budget unless approved by MCC. Significant reduction in the inputs under the Fixed Amount portion of the Grant including changes to key personnel or significant reduction in the level of time commitment could result in an amendment to the Grant Agreement reducing the level of funding support committed by the MCA Entity.
- Cost Reimbursement Grant - reduction in Grant Activities or deliverables The MCA Entity cannot modify the Grant Agreement to reduce the Grant Activities or deliverables without a corresponding reduction of the ceiling amount of the Grant unless approved by MCC.
Follow-on Awards/Extensions
A follow-on award is a modification to a grant award to provide for the continuation of successful and currently supported programs beyond the original Grant period and funding level. A follow-on award must be within the objective or purpose of the original Grant Activities and cannot be a major shift in technical focus or content from the original Grant. A follow-on award supports the same Grant Activities or Grant Activities that are a natural extension of and closely related to the Grant Activities in the original Grant. A Grant Award to add new and different Grant Activities that are outside the objective or purpose of the original Grant does not qualify as a follow-on award but is considered a new award that must be competed or justified as a Direct Request. Follow-on awards may include an increase in funding, time and/or activities. Any increase in funding of more than 25 percent requires MCC approval.In requesting MCC approval of a follow-on award, the MCA Entity must provide evidence that (1) continuing support is still relevant and meritorious, (2) the Grantee has substantially and successfully carried out the original Grant including successful financial management of the Grant, and (3) the lessons learned and capacity built by the Grantee in carrying out the original Grant will contribute to the impact and effectiveness of the follow-on award. Higher scrutiny will be given if the original Grant was not previously competed.
If the previous award has ended, the start date of the follow-on award should be instituted concurrent with the original expiration date so that the support is continuous and there is no break in funding.
Suspension and Termination
- Suspension
Suspension means the temporary stoppage of Grant Activities and disbursement as ordered by the MCA Entity.The MCA Entity may suspend the Grant to permit the Grantee to cure an allegation of noncompliance. The MCA Entity must suspend a Grant immediately and notify MCC if the MCA Entity discovers:
- A material omission, incorrect statement or other misrepresentation in the Grantee’s application that materially influenced the decision to award the Grant, or
- A material violation of the Grant Agreement due to fraud, misconduct or material mismanagement of funds.
Suspension must be for a fixed period which can be changed by the MCA Entity by subsequent written notice. Suspension does not extend the end date of the Grant unless the Grant is formally modified to set a new end date.
- Termination
Termination of a Grant means the ending of a Grant, in whole or in part, at any time before the planned end date of the Grant. The MCA Entity must provide in the Grant Agreement that the Grant may be terminated by the Grantee, or by the MCA Entity or by mutual consent. In the case of termination by either party and for any reason, the closeout responsibilities of the Grantee and the MCA Entity continue, including, but not limited to, property management, disposition of assets, submission of reports, and reconciliation of costs and payment.
- Termination by the Grantee A Grantee may unilaterally terminate a Grant, in whole or in part. If a Grantee seeks to terminate only part of a Grant, the MCA Entity may determine to terminate the entire Grant.The Grantee must provide at least 30 calendar days for notice of termination in writing. In the notice of termination, the Grantee must state the reasons for termination and the proposed terms. The MCA Entity must have 10 calendar days to respond in writing to the proposed terms. The MCA Entity may accept the terms as proposed by the Grantee or proposed alternative terms. The Grantee must have 5 days to respond in writing. Unless the parties have agreed in writing to cancel the termination or to set a date for termination, the Grant will terminate 30 calendar days after the notice of termination was received by the MCA Entity.
- Termination by Mutual Consent The MCA Entity and the Grantee may mutually agree to terminate a Grant, in whole or in part. The agreement to terminate the Grant must be in writing, stating the effective date and, in the case of partial termination, the portion of the Grant to be terminated.
- Termination by the MCA Entity
The MCA Entity may terminate a Grant, in whole or in part, if the Grantee materially fails to comply with the terms and conditions of the Grant Agreement, if the Grantee becomes financially insolvent or if there are circumstances as determined by the MCA Entity that require termination of the Grant.
- Process for termination for noncompliance: If the MCA Entity determines to terminate a Grant for noncompliance, it must give the Grantee written notice of termination, in whole or in part, stating the reasons for the termination and the effective date of the termination. A copy of the notice must be submitted to MCC. Material noncompliance does not require an allegation of misconduct. The failure to comply may be material either in a singular material deficiency or cumulative deficiencies that when taken together are deemed material.The MCA Entity must give the Grantee a reasonable opportunity to refute the allegation of noncompliance. To refute an allegation of noncompliance, the Grantee must substantiate that the determination of noncompliance is founded on a substantial factual error. An allegation of noncompliance cannot be refuted by defense of honest mistake, good intention, or ignorance of the requirement(s).
If the allegation of noncompliance is not associated with allegation of fraud or misconduct, the MCA Entity may give the Grantee an opportunity to cure the noncompliance, but this is not required. If the allegation is associated with fraud or misconduct, the MCA Entity may not give the Grantee an opportunity to cure the noncompliance unless approved by MCC.
- Process for termination of the Grant for insolvency: The MCA Entity must terminate a Grant if the Grantee becomes insolvent. The MCA Entity must give written notice of termination to the Grantee that provides for immediate termination of the Grant and suspension of any disbursement until there is final settlement and closeout. The MCA Entity must take special care to oversee closeout of the Grant particularly related to property management and disposition of assets.
- Process for termination by necessity of MCA Entity: If the MCA Entity determines for its own purposes that it needs to terminate the Grant, in whole or in part, it must give the Grantee written notice of termination stating the reasons for the termination and the effective date of the termination. In the event of a partial termination, the notice must also identify which parts of the Grant are being terminated. In setting the termination date, the MCA Entity should try to maximize the benefit of Grant funds taking into consideration that the Grantee is entitled to receive disbursement of all costs incurred or milestones achieved as of the date of termination and a pro-rata share of any deliverables or costs in progress.
- Process for termination for noncompliance: If the MCA Entity determines to terminate a Grant for noncompliance, it must give the Grantee written notice of termination, in whole or in part, stating the reasons for the termination and the effective date of the termination. A copy of the notice must be submitted to MCC. Material noncompliance does not require an allegation of misconduct. The failure to comply may be material either in a singular material deficiency or cumulative deficiencies that when taken together are deemed material.The MCA Entity must give the Grantee a reasonable opportunity to refute the allegation of noncompliance. To refute an allegation of noncompliance, the Grantee must substantiate that the determination of noncompliance is founded on a substantial factual error. An allegation of noncompliance cannot be refuted by defense of honest mistake, good intention, or ignorance of the requirement(s).
- Effects of Suspension or Termination The Grant Agreement must provide that costs incurred by the Grantee resulting from obligations incurred by the Grantee during a suspension or after termination of the Grant are not allowable and will not be reimbursed by the MCA Entity unless the MCA Entity expressly authorizes them in the notice of suspension or termination or subsequently. However, if specifically stated by the MCA Entity in the notice of suspension or termination, disbursements to the Grantee during suspension or after termination may be allowable if the costs results from obligations which were properly incurred by the Grantee before the effective date of suspension or termination and the cost would be allowable if the Grant was not suspended or terminated.
Dispute Resolution
- Resolution of Disputes by Mutual Agreement If disputes, disagreements, and misunderstandings arise during the administration of a Grant, the Grantee and the MCA Entity must attempt to resolve the issue(s) by discussion, negotiation and mutual agreement as soon as practicable. The MCA Entity may seek assistance of an independent party to help negotiate a resolution based on mutual agreement of the MCA Entity and the Grantee.
- Claim to the MCA Entity
If the MCA Entity and the Grantee fail to resolve a dispute by mutual agreement, the Grantee may submit a claim arising out of or relating to its Grant.
- Submission of Claim:
The claim must:
- be submitted in writing to the MCA Director of Grants,
- specify the nature of and basis for the relief requested,
- include all data that supports the claim, and
- describe the reasons that the claim was not resolved by mutual consent.
- Decision of MCA Entity: Within 30 calendar days of receipt of the claim, the MCA Entity must issue a written decision stating the reasons for the decision and identify the information upon which the decision is based. The decision will be made solely on the basis of the written record unless the deciding official determines to conduct a fact-finding procedure or an oral hearing. If more time is required, the MCA Entity must provide written notice to the Grantee stating a specific date when the MCA Entity will render a decision.The official rendering the decision for the MCA Entity must be a high-level official that was not involved in the earlier discussions attempting to settle the dispute by mutual agreement. This decision is a final decision of the MCA Entity.
- Submission of Claim:
The claim must:
- Alternative Dispute Resolution If the parties are unable to resolve any claim, controversy, or other dispute regarding their legal rights and obligations, the Grant Agreement must include a broad form, mandatory, binding arbitration clause under which the parties do consent to the jurisdiction of the International Chamber of Commerce. While the Grant Agreement must be governed by the substantive laws of the Compact country, the arbitration clause will provide that the arbiters may look to the UNIDROIT Principles of International Commercial Contracts to fill any gaps in the applicable law.
Grant Closeouts
Grant Closeout RequirementsGrant closeout is the process that the MCA Entity and the Grantee must follow after the Grantee has completed all Grant Activity. The closeout process includes financial closeout, property disposition and reporting. The Grant closeout process must accurately address the following:
- The determination that the Grant Activities are completed.
- The reconciliation of funds owned to the Grantee or to be returned to the MCA Entity.
- The disposition of property acquired with Grant funds.
- The final reporting as required by the terms and conditions of the Grant Agreement.
- The MCA Entity should complete the closeout process for all Grants no later than 60 days prior to the Compact End Date.
- The MCA Entity must give the Grantee written notice of the closeout procedures and documentation requirements at least 60 days prior to the end date of the Grant. This notice must inform the Grantee of the following:
- End date of the Grant by which all Grant Activity must be completed and after which no further activity or costs will be incurred or reimbursed.
- Date by which the Grantee must submit final financial report, payment requests, Grant completion report and a final inventory report in the format of the template attached to the notice.
- Date by which Grantee must return any funds due back to the MCA Entity.
- Notice that the Grantee may be subject to a final audit as part of the closeout activity and before final disbursement is made.
- Duty of Grantee to retain Grant records for period as stated in the Grant Agreement.
- Schedule of final site visit and closeout meetings.
- The MCA Entity must ensure that the final completion report is accurate and complete.
- The MCA Entity must verify the inventory report and give instructions for disposition of assets.
- Before making final disbursements, the MCA Entity must ensure that all reports and deliverables have been received and accepted, that assets have been disposed as instructed and that refunds due the MCA Entity have been paid or are deducted from final disbursement.
- The MCA Entity will conduct a final closeout review to confirm that all closeout procedures have been completed.
- The MCA Entity will give the Grantee final written notice that the closeout of the Grant is complete.
Attachment A. Program Grant Guidelines Approval Matrix
| PGG Reference | Decision | MCA Entity | Governing Body of MCA Entity | MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part 1 | Use of Grant instrument instead of Procurement | All (unless approved when Compact is signed) | All (unless approved when Compact is signed) | All(unless approved when the Compact is signed otherwise MCC’s approval is documented when it provides no objection to the MCA’s Grants Operations Manual and amendments) |
| P2.1.2.4(4) | Grant Award or Grant Subaward to a local public, publicly owned or publicly subsidized entity | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P2.1.2.4 (8) | Grant Award or Grant Subaward to a Public International Organization | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P2.1.2 (5) | Application of Program Income | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P2.1.2 (8) | Grantee’s branding and marking plan | All | none | none |
| P2.1.2 (10) | Waiver of PGG provision | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P3.1.1(2) | Grants Operations Manual and material amendments(Material amendment is amendment that add a new Grant Program or significantly changes the terms and conditions of previously approved Grant Program.) | All | All | All |
| P3.1.1 (3) | Grants Schedule and Amendments | All | All (except when by-laws limit approval of Amendments) | All |
| P3.1.1 (4) | Grants Notices (Request for Applications, Calls for Concept Papers, and Notice of Funding Opportunities) | All | None | If required as condition in the Grant Program |
| P3.1.1 (4) | Designating an alternative website other than the MCA Entity’s website for posting of required Grant notices | Once | Once | Once |
| P3.1.1 (7) | Use of Co-Creation | All | If required in by-laws | Only if MCC requires pre-approval as condition in a specific Grant Program |
| P3.1.1 (9) | Merit Review Panel | All | None | Only if MCC requires pre-approval as condition in a specific Grant Program |
| P3.1.1 (13) | Appointment of Selection Committee | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P3.1.1 (13) | Selection Committee Concept Selection Report | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P3.1.1(13) | Selection Committee Grant Award Report | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P3.1.1(13) | Amendments to Selection Committee Concept Selection Report | All | If required in by-laws | Only if the amendment deletes or adds Proposer |
| P3.1.1(13) | Amendments to Selection Committee Grant Award Report | All | If required in by-laws | Only if the amendment deletes or adds an Applicant or if the amendment, or cumulative amendments, increases or decreases a proposed Grant amount by more than 10 percent |
| P4.1.3(6) | Grant Award based upon Direct Request | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P4.1.3(7) | Grant Award based upon Unsolicited Application | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P4.2 | Memorandum of Negotiation documenting changes to the terms and conditions of the Grant Agreement from the original instructions of the Selection Committee as set out in the approved Selection Committee Grant Award Report | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P5.1.1.1 (b) (iv) | Use of In-Kind Grant as a substitute for advance disbursement | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P5.1.1 (2) (3) (4) | Change of Grantee’s key personnel or significant reduction in level of time commitment of key person as set out in Grant Agreement for Fixed Amount Grant, Fixed Amount Grant with Reimbursement of Direct Costs or Cost Reimbursement Grant | All | None | If required as condition in approval of the Grant Program |
| P5.1.2 (4) | Use of Grant with Substantial Involvement (Cooperative Agreement) | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P5.1.2 (4) | Final terms of Grant with Substantial Involvement (Cooperative Agreement) before signed | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P5.1.2 (5) | Use of Grant with Limited Involvement | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P5.1.2 (5) | Final terms of Grant with Limited Involvement before signed | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P6.1 (7) | Grantee’s procurement system | All (if Grant requires the Grantee to procure goods, works or services from third party) | None | Only if MCC requires pre-approval as condition in a specific Grant Program |
| P6.1.8 (1) | Grantee use of Subaward instead of procurement | All | None | None |
| P6.1.8(2) | Subaward Agreement that passes through all or most of the key responsibilities to carry out the Grant | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P6.1.8 (3) | Subaward Agreement under which the Subrecipient joins the Grantee in carrying out the Grant | All | None | All (unless the Subaward arrangement was identified in the Grant Application and Grant Budget that was previously reviewed when MCC approved the Selection Committee Grant Award Report) |
| P6.1.10 (1) | Assignment of Grant | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P6.1.10 (2) | Modification of Grant to increase beneficiary community | All | If required in by-laws | If increase is more than 10 percent. |
| P6.1.10 (3) | Time or period extension without additional funding | All | If required in by-laws | If the time extension is 25 percent or more of the original Grant or 25 percent more of the last amendment. |
| P6.1.10 (4) | Modification of Grant Agreement to realign Milestone Disbursement Schedule without additional funding | All | If required in by-laws | If transfer of funds exceeds 25 percent of total amount of the Grant. |
| P6.1.10(5) | Modification of Grant Agreement to increase amount of Grant or Grant ceiling without increase in Grant Activity or deliverables. (Except for In-Kind Grants) | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P6.1.10(6) | Modification of In-Kind Grant to increase the Grant amount to actual cost of goods, works or services above the estimated costs | All | If required in by-laws | Increase of Grant by more than 20 percent |
| P6.1.10 (7) (8) (9) | Modification of Grant Agreement to reduce Grant Activities or deliverables without corresponding reduction of Grant amount or Grant ceiling | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P6.1.11 | Follow-on Awards/Extension | All | If required in by-laws | All |
| P6.1.11 | Follow-on Awards/Extension | All | If required in by-laws | Increase in funding of more than 25 percent |
| P6.1.12(2-c-i) | Give a Grantee an opportunity to cure noncompliance associated with fraud or misconduct | All | All | All |

