| (in millions of $) | FY 2022 | FY 2023 | FY 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enacted | Enacted | Request | |
| Total Appropriation/Request | 912.0 | 930.0 | 1,073.0 |
| Total Compact Assistance | 647.5 | 651.0 | 760.0 |
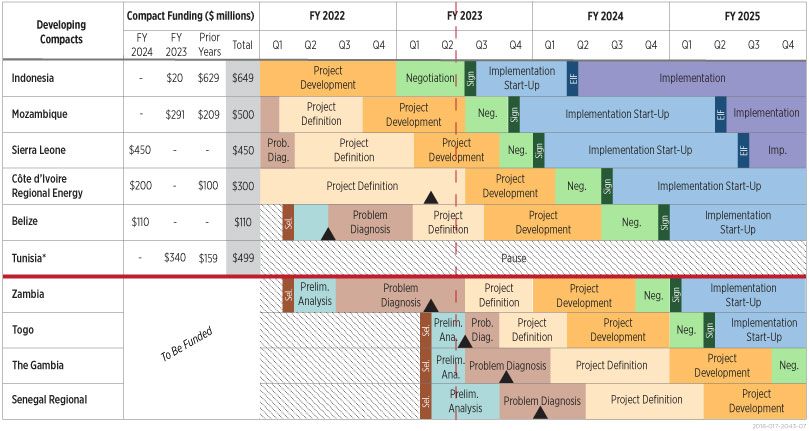
In FY 2024, MCC requests $760 million to support compact assistance for Sierra Leone, Côte d’Ivoire Regional Energy, and Belize, which will be past their critical project definition phases and into completing development during FY 2024.
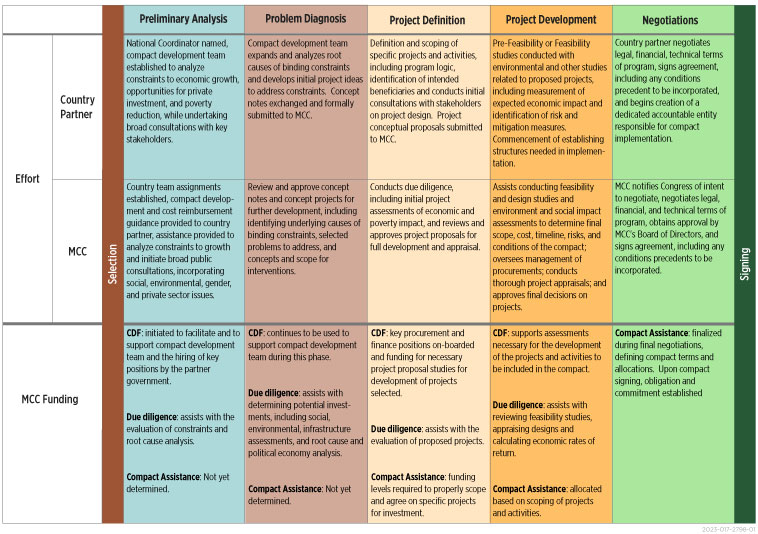
MCC anticipates eleven compacts undergoing implementation, with another five signed or presented to MCC’s Board, and ready to be signed by the end of FY 2024. This includes the Indonesia compact which will sign shortly and enter into force next fiscal year and the Mozambique compact projected to sign later this fiscal year. Looking ahead, MCC currently has eight unsigned compacts in different phases of development, including the Tunisia compact currently paused. FY 2024 funding will establish budgets for three of the seven as yet unfunded programs, leaving four compacts undergoing compact development to be funded, including Zambia, Togo, The Gambia, and Senegal regional program. Throughout the compact development processes, MCC and country partner resources are being invested prior to compact assistance funding being received.
The following chart provides the pipeline of all compacts not yet signed:
- : Compact Development Funding (CDF) Grant Agreement with partner country signed
- Sel.: Selection of eligible partner country to develop compact by MCC’s Board of Directors
- Sign: Signing of Compact Grant Agreement with partner country
- EIF: Entry into Force of Compact and beginning of compact implementation
* Tunisia compact signing was paused in July 2021 due to concerns about democratic governance. MCC’s Board reviews the status regularly, and existing funds continue to be planned and held under the Tunisia compact at the time of this submission. Given the duration of this pause, MCC recognizes that fresh diligence or scoping would be required to proceed with the compact and as a result, MCC anticipates other compacts in development may reach a readiness stage before Tunisia. This may lead MCC to reprogram such funding to other compacts that are ready sooner in the coming fiscal years, including Sierra Leone, Zambia, and Togo.
Indonesia
On the sidelines of the G20 in Bali in November, President Biden announced that MCC and the Indonesian government had successfully negotiated a compact to improve the financing of infrastructure, particularly transport and logistics infrastructure, and increase access to finance for micro-, small and medium enterprises. The $649 million Indonesia Infrastructure and Finance Compact was approved by the MCC Board at its December meeting and the MCA-Indonesia II Board of Directors appointed later that month. MCA-Indonesia II is intending to hold its first board meeting, hire its first round of staff, and sign initial contracts before the end of March 2023, with compact signing planned soon thereafter. Following compact signature and a major effort to finalize MCA-Indonesia II establishment, the Government of Indonesia and MCC will continue project refinement and feasibility study work in support of an ambitious timeline for entry-into-force, planned for early Q2 FY 2024.
Results from Indonesia’s 2011 Compact
MCC’s initial compact in Indonesia closed in April 2018. During the five-year term of the compact program, the GOI government of Indonesia disbursed $474 million to support modernization of public procurement functions, improvements in health and nutrition, and sustainable energy and resource management. The nutrition project trained over 17,500 providers on prenatal health services; distributed medical supplies; and conducted over 4,200 community sanitation behavior change meetings across 64 districts to combat low birth weight, childhood stunting, and childhood malnourishment. The procurement modernization project trained over 1,000 procurement professionals (24% percent of whom are women) to apply modern procurement and management skills in the national and local governments in ways that will increase procurement quality and achieve substantial savings. The energy project established a market-responsive grants financing facility that supported 66 projects for renewable energy, peatland restoration, sustainable agriculture, and improved natural resource management. The project also trained over 127,000 farmers (including over 43,000 women) in climate-smart agriculture, natural resource management, social forestry, and renewable energy. The implementation of the compact program reinforced community ownership and innovation through flexible, scalable approaches that allowed for emerging opportunities. The Indonesia Compact Star Report is linked here.
Mozambique
MCC and the Government of Mozambique are finalizing the designs of three projects that will address the constraints to economic growth of (1) poor agricultural policy, legal and regulatory framework, and (2) poor and climate-vulnerable secondary and tertiary road infrastructure and low freight transport market competitiveness. One project aims to improve road transport by providing climate-smart, sustainable, and cost-effective road transport connectivity and reforms for a second-generation road fund. Another project includes targeted support for improving the business enabling environment as well as creating an investment platform to connect commercial aggregators to smallholder farmers under a results-based financing arrangement. The third project plans to leverage both existing partners and climate finance to holistically reverse the decline in coastal fisheries and enhance the benefits to local communities. MCC aims to submit the Compact to its Board in June 2023.
Results from Mozambique’s 2008 Compact
MCC’s first compact in Mozambique closed in September 2013, with final disbursements of $448 million. The compact increased the country’s economic growth and reduce poverty by investing in four project areas: 1) water and sanitation, 2) roads, 3) land tenure, and 4) agriculture. Under the compact, project teams constructed more than 614 rural water points, upgraded and expanded two municipal drainage systems, and upgraded and expanded two urban water supply systems. The compact also funded the construction of 253 kilometers of improved roads, the mapping of nearly 8.8 million rural hectares of land, and the formalization of nearly 150,000 urban land titles. Furthermore, the compact supported the training of 15,000 farmers in pest and disease surveillance and control and planted 780,000 disease-resistant seedlings. MCC anticipates the compact to benefit over 2,600,000 Mozambicans over 20 years. The Mozambique Compact Closed Compact Report is linked here.
Sierra Leone
MCC and the Government of Sierra Leone are developing a compact to address the country’s power constraint, building on work in the energy sector completed under MCC’s Sierra Leone Threshold Program that closed in 2021. Four potential projects are currently under consideration for MCC investment. One project seeks to expand Sierra Leone’s electricity transmission grid with new, climate-resilient infrastructure. Another project aims to increase the generation of energy in Sierra Leone, including through potential support for targeted investments in solar and hydro power projects. A third project aims to improve the resilience and stability of Sierra Leone’s limited existing distribution network, and potentially expand the network to new customers. This project will also include a focus on increasing the productive use of energy to reduce food insecurity via improved post-harvest processing and storage of key crops. The fourth project will support the government’s efforts to plan and coordinate energy sector investments, ensuring the sustainability of MCC projects and activities. MCC expects to be in final negotiations in the summer of 2023 and aims to submit the compact to MCC’s Board of Directors for approval in the fall of 2023.
Côte d’Ivoire Regional Energy
MCC is developing a concurrent compact program for regional integration with Côte d’Ivoire, in partnership with entities of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), including the West African Power Pool, the future Information and Coordination Center, and the ECOWAS Regional Electricity Regulatory Authority. MCC is currently assessing potential projects and exploring investments in power sector reform, infrastructure, and capacity building in Côte d’Ivoire to solidify its role as an anchor power exporter to the West African region.
MCC plans to make an investment decision on the Côte d’Ivoire Regional Energy program, with Côte d’Ivoire as an anchor power exporter, by September 2023; negotiate a compact in December 2023; and seek MCC Board approval in March 2024.
Belize
In December 2021, MCC’s Board of Directors selected Belize as eligible to develop a compact. The Government of Belize quickly appointed a national coordinator and hired a strong team of local counterparts who have worked closely with MCC to conduct the constraints analysis and root cause analysis. Based on these assessments, MCC and its counterparts in Belize are working closely to develop projects in the education and electricity sectors. The education project will focus on increasing the availability of post-primary graduates with the knowledge, skills, and values relevant to current and anticipated labor market demands. The electricity project will focus on decreasing the wholesale cost of electricity and ensuring that these cost savings are passed on to consumers in retail tariffs. MCC and the Government of Belize are now preparing for the launch of several studies to further develop the proposed projects. MCC has successfully piloted several compact development acceleration changes in the Belize process and is thus targeting Board approval and compact signing by September 2024.
Tunisia
While MCC’s Tunisia program development is currently paused, the proposed Tunisia compact features two projects focused on addressing Tunisia’s constraints to growth. The Transport and Trade Project has been designed to make it easier and less expensive for businesses to engage in trade in Tunisia and includes investments to improve management and expand infrastructure at the Port of Rades, Tunisia’s principal port. It would also simplify and digitize trade procedures and regulations in the transport and trade sectors. The Water Project has been designed to improve sustainable use of scarce groundwater resources, while moving the country toward improved water sustainability. The compact program also integrates gender and social inclusion by improving market access for women-owned enterprises.
MCC’s Board approved the Tunisia compact in June 2021, but MCC put signature of the compact on hold following the President of Tunisia’s dismissal of the Prime Minister and freezing of Parliamentary activities on July 25, 2021. Development of the proposed MCC compact remains paused due to concerns about democratic governance, but MCC would welcome the opportunity to advance the compact once the Government of Tunisia has taken steps to align with MCC’s eligibility criteria. Should the Government take such steps and were MCC to resume compact development, MCC anticipates the need for significant work to address developments over the past 18 months that are likely to have affected the original compact design, including global inflation and supply chain disruptions.
MCC’s Board reviews the status regularly, and existing funds continue to be planned and held under the Tunisia compact at the time of this submission. Given the nature and duration of the pause and the need for diligence or scoping work described above, MCC anticipates other country compacts in development may reach a readiness stage before Tunisia. This may lead the agency to reprogram such funding to other compacts that are ready sooner in the coming fiscal years, including Sierra Leone, Zambia, and Togo.
Zambia
In December 2021, MCC’s Board of Directors selected Zambia as eligible to develop a new compact, following free and fair national elections in August 2021 and successful closure of the prior compact in November 2018. MCC and the Government of Zambia identified the binding constraints to growth of agriculture inputs and policies, poor roads and transport, and low access and reliability of power, and are now exploring strategic interventions in the areas of transportation and logistics, agricultural policy reform, and access to finance. MCC will soon be entering the critical project definition phase which requires budget clarity and will submit the compact to MCC’s Board of Directors for approval in September 2024, with compact signing expected in the first quarter of FY 2025.
Results from Zambia’s 2018 Compact
MCC’s previous compact in Zambia closed in November 2018, with final disbursements of $332 million. The compact focused on urban water, sanitation, and drainage infrastructure and strengthening the Zambian government’s capacity to effectively manage the water and sanitation sector in the capital city of Lusaka. MCC and the Zambian government rehabilitated a water treatment plant along the Kafue River—which, at the time, provided 40 percent of Lusaka’s clean water—and built nearly 150 miles of water and sewage main pipelines. The compact funded the upgrade and expansion of key sewage treatment ponds, supporting an estimated 156,000 residents—which is roughly eight times more than its previous capacity for 18,000. The compact is expected to benefit 1.2 million people over 20 years. Given the positive impact from a hybrid solar-powered water system supported by the compact, the Lusaka Water and Sewage Company installed two small solar pumping water systems in 2021 and plans to install additional systems, expanding access to a reliable source of water to homes and businesses in additional communities. The Zambia Star Report is linked here.
Togo
MCC’s Board selected Togo as eligible to develop a compact at its December 2022 meeting. MCC is currently working with the Government of Togo to identify the binding constraints to economic growth that can be addressed through a compact program. Togo is part of a pilot approach to further fast track the compact development process, building on compact development acceleration efforts over the past two years. With the current threshold program focused on digital and information communication and technology, the compact development team is including an exploration of synergies in this sector while conducting the constraints analysis.
The Gambia
MCC’s Board selected The Gambia as eligible to develop a compact at its December 2022 meeting. The Government named a national coordinator in January 2023 and allocated funding to support the stand-up of its team. MCC is currently working with the Government of The Gambia to identify the binding constraints to economic growth that can be addressed through a compact program.
Senegal Regional
Senegal was selected by the MCC Board of Directors as eligible to develop a concurrent regional compact in December 2022. MCC is currently working with the Government of Senegal to identify the constraints to regional integration, collaboration, and trade that can be addressed through a compact program.

